Active RFID design based on MSP430 and CC1100
Radio frequency identification (Radio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon, RFID) technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology using wireless radio frequency communication. Compared with the currently widely used barcode technology, RFID has large capacity, long recognition distance, strong penetration ability, Strong anti-fouling characteristics. RFID technology has developed more maturely and gained large-scale commercial use. With the introduction of RFID portable devices, power consumption has become an important issue. This article will elaborate on the hardware and software implementation of bidirectional active tags based on the MSP430F2012 and CC1100 low-power design concepts.
1. Low power design
1.1 Low power consumption overview
Power consumption is basically defined as the rate of energy consumption, which can be divided into two categories: transient power consumption and average power consumption. The two have different meanings, have different application backgrounds and optimization strategies, and are generally summarized as low-power designs. The actual research can be divided into:
(1) Transient power optimization: The goal is to reduce peak power consumption and solve circuit reliability issues.
(2) Optimization of average power consumption: The goal is to reduce energy consumption within a given time, mainly for battery-powered portable electronic devices, to extend battery life or reduce device weight.
1.2 Physical sources of power consumption
The power consumption of the chip circuit mainly comes from two aspects: dynamic power consumption and static power consumption. The dynamic power consumption is mainly the charging and discharging of the capacitor and the short-circuit current. Static power consumption is mainly leakage current, including PN junction reverse current and sub-threshold current, and penetration current. If the working timing and software algorithm design are defective, it will reduce the system's working efficiency, extend working time, and directly increase the system's energy consumption.
1.3 Low-power design strategy
Algorithm-level power optimization: At the beginning of the circuit design, it is necessary to choose the algorithm, you should try to choose an algorithm with high power consumption efficiency. First of all, from the perspective of the size of the logic required to implement the algorithm, the fewer the number of operations, the required bandwidth, storage operations, and port operations in the algorithm, the lower the power consumption of the circuit to which this algorithm is applied. In actual design, the overall performance and power consumption need to be balanced according to the requirements of the application. At the same time, the co-processing required in the algorithm must be considered. The simpler the co-processing required by the algorithm, the fewer collaboration modules, and the lower the power consumption required to implement the algorithm. In addition, fewer temporary variables in the algorithm, short time for temporary variables to be effective, and reasonable use of loops will reduce the power consumption required by the algorithm.
System-level power design and management: System-level power management is mainly dynamic power management. The usual approach is to operate in a sleep state when in an idle state, and only some devices are in operation; when an interrupt is generated, other devices are awakened by this interrupt. In fact, this part needs the support of hardware, such as the low power consumption technology of the power system; the division of system software and hardware is to decide which functional modules are realized by software with lower power consumption and which functional modules are realized by hardware with lower power consumption ; The choice of low-power processors.
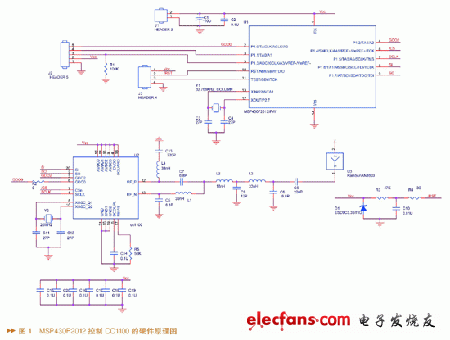
2. System hardware design
Comprehensively considering the source of system power consumption and low-power design strategies, the hardware design selects single-chip computers and RF transceiver chips with low power consumption characteristics, and simplifies the circuit as much as possible to reduce power consumption expenses.
More stable performance
Disposable ecig have a completely enclosed design, reducing the need for charging and replacing cartridges. The no-charge design also reduces the occurrence of faults. It is understood that with rechargeable e-cigarettes, each cartridge needs to be charged at least once and the battery efficiency is extremely low, while the design of disposable ecig can solve this problem very well.Disposable ecig are very easy to carry on daily trips, no need for any operation in the use of airflow induction, direct suction can be out of smoke, meaning that you just need to suck directly on the hand can be the main feature of the small cigarette is practical portability is the main, its appearance is very small, no longer like the previous big smoke box mechanical rod nowhere to put.
The market outlook for disposable ecig
There has been a controversial topic regarding the use of disposable ecig. According to scientific studies, the long-term use of e-cigarettes can cause harm to the human body, no less than tobacco. Therefore, it is important not to overuse either type of e-cigarette - after all, smoking is bad for your health. Specifically, the PMTA requires that any new tobacco product be approved by the FDA for legal promotion and that the FDA consider all aspects of the product to be beneficial to public health. Our products can always be sold under the supervision of the PMTA at cost and are prohibited for sale to minors. We have strict guarantees regarding the quality of our products.
Disposable E-Cig,Disposable Vape Pen Oem,Best Disposable Vapes,One-Time Use Vape
Shenzhen MASON VAP Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.cbdvapefactory.com