Prevent car USB circuit battery short circuit failure - Part 1
Automakers continue to use infotainment systems as an extension of the multimedia experience. The USB interface has been an essential element of the infotainment architecture, so manufacturers have embraced this already consumer-centric interface with stricter protection requirements. There is a need to prevent short-circuiting of the vehicle battery during assembly, manufacturing or maintenance. For example, when the long wire harness that connects the head unit to a different connection module is damaged, all pins can be shorted to a 12V car battery. Other potential failure mechanisms include the use of non-compliant adapters, cables or chargers; mechanical distortion of the USB connector or cable; or any debris that enters the connector and shorts the data line to VBUS.
In the first part of a two-part series, I will illustrate the best way to prevent short circuit failures in USB circuit cells. In my next post, I will extend the best way to optimize your car's USB battery short-circuit design.
When designing a battery-proof short-circuit USB, always keep in mind three main aspects:
· Protect the bandwidth of the solution.
· Clamp voltage and response time behavior.
· Overcurrent and short-to-ground characteristics.
In the past, it was impossible to find a USB 2.0 anti-battery short-circuit solution that would solve all three aspects, but TI's new TPD3S714-Q1 series of anti-battery short-circuit protection devices can help solve these common problems.
bandwidth
Signal integrity is one of the biggest challenges designers face in automotive USB applications. Since USB 2.0 supports data transfer rates of up to 480 Mbps, any small amount of capacitance added to the wires can distort the signal, causing data transfer failures. This complicates the designer's task in finding a solution that not only protects sensitive electronics from high voltage and current spikes, but also maintains optimal signal integrity.
The TPD3S714-Q1 is a single-chip solution for VBUS and data line protection against battery shorts, short circuits and electrostatic discharge (ESD) for USB connectors. The integrated data exchange provides twice the high bandwidth for minimal signal attenuation while providing up to 18V protection against battery shorts. Figure 1 is an insertion loss diagram highlighting high-speed data exchange using a 1GHz-3dB bandwidth.
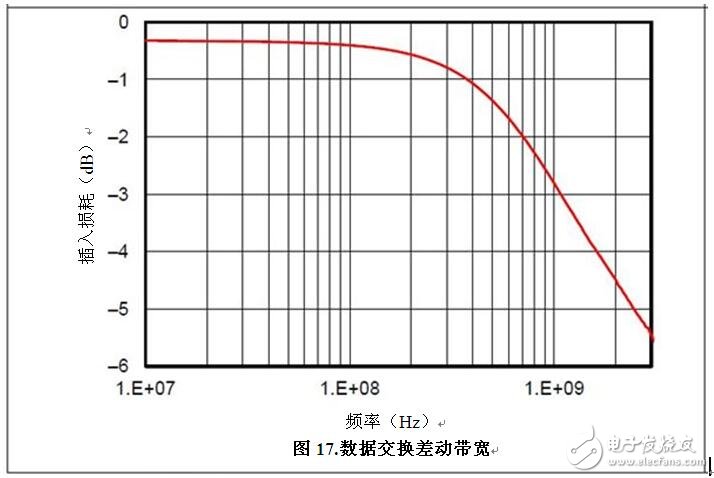
Figure 1: TPD3S714-Q1 Data Exchange Differential Bandwidth
You can use an eye diagram to analyze the effect of line capacitance on bandwidth. Measuring minimum and maximum voltage levels and jitter can expose any problems in USB data line transmission. The high 1GHz bandwidth allows USB 2.0 high speed applications. A small margin above the 720MHz bandwidth also helps maintain a common clear USB 2.0 eye diagram with a long stay in a car USB environment. Figure 2 is an example of a USB 2.0 eye diagram.
  
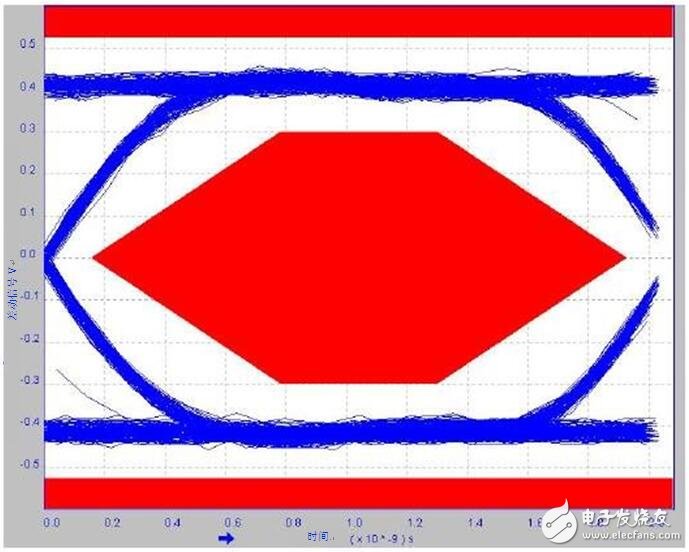
Figure 2: USB 2.0 Eye Diagram of the TPD3S714-Q1
Catering to the ever-changing demands of our patrons, we are offering them a comprehensive range of Hot Dip Galvanized Radiator. These are manufactured as per latest market trends so as to ensure their wide applications in industries. Offered products are highly demanded by the clients for their excellent design, longer service life and durability.
Galvanizing is a way of defending a steel surface from corrosion by delivering a surface coat of Zinc. The process is carried out by dipping the radiator in molten zinc bath which is upheld at a temperature of about 450 degrees.
In long-term, continuous exposure, the recommended maximum temperature for hot-dip galvanized steel is 200 °C (392 °F), according to the American Galvanizers Association. The use of galvanized steel at temperatures above this will result in peeling of the zinc at the inter metallic layer.Hdg Radiator,Oil-Immersed Hdg Radiator,Hot-Dip Galvanizing Radiator,High-Performance Hot Dip Galvanized Radiator
Shenyang Tiantong Electricity Co., Ltd. , https://www.ttradiator.com