Introduction to Multipurpose 555 Time Base Integrated Circuits
The internal circuit of the 555 circuit contains two voltage comparators, a basic RS flip-flop, and a discharge switch T. The comparator's reference voltage is provided by a voltage divider consisting of three 5K resistors. They make the reference level of the non-inverting input of the high level comparator A1 and the inverting input of the low level comparator A2 2/3 VCC and 1/3 VCC, respectively. The outputs of A1 and A2 control the state of the RS flip-flop and the state of the discharge tube switch. When the input signal is from the 6 pin, that is, the high level triggers the input and exceeds the reference level 2/3VCC, the flip-flop resets, the output of the 555 pin 3 outputs a low level, and the discharge switch tube is turned on; when the input signal is from 2 The input of the pin is lower than 1/3VCC, the trigger is reset, the 3 pin of 555 outputs high level, and the discharge switch tube is cut off. The 555 timer RD is the reset terminal. When RD=0, 555 outputs a low level. Usually the RD end is open or connected to VCC.
We know that 555 circuits can be generalized into three categories in terms of application and working methods. There are many different circuits for each type of work. In practical applications, in addition to a single type of circuit, many different circuits can be combined, such as multiple monostable, multiple bistable, monostable and unstable, bistable and unstable combinations. As a result, the circuit becomes more complicated. In order to facilitate our analysis and identification of the circuit, a better understanding of the 555 circuit, here we classify and generalize according to the structural characteristics of the 555 circuit, the 555 circuit is divided into 3 categories, 8 kinds, a total of 18 unit circuits. In addition to drawing its standard patterns, each circuit indicates their structural characteristics or identification methods, and gives calculation formulas and their uses. It is convenient for everyone to identify and analyze the 555 circuit. These three types of circuits will be introduced separately below.
The monostable circuit has a single-stable operation, which can be divided into three types. See the illustration.
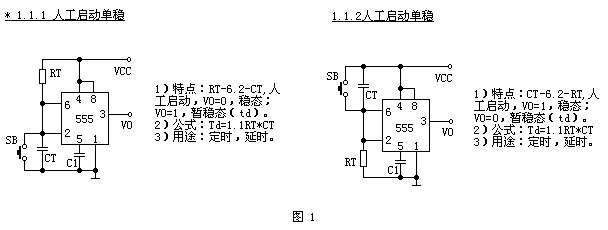
The first type (Fig. 1) is a manual start monostable, and is divided into two different units due to the different timing resistor timing positions, and is coded by 1.1.1 and 1.1.2, respectively. The form of their inputs, that is, the structural characteristics of the circuit are: "RT-6.2-CT" and "CT-6.2-RT".
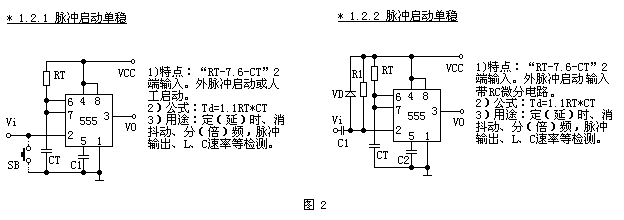
The second type (Fig. 2) is a pulse-start type monostable, and can also be divided into two different units. Their input features are "RT-7.6-CT", which are input from the 2nd end. 1.2.1 The 2nd end of the circuit has no components and has the simplest form; the 1.2.2 circuit has an RC differential circuit.
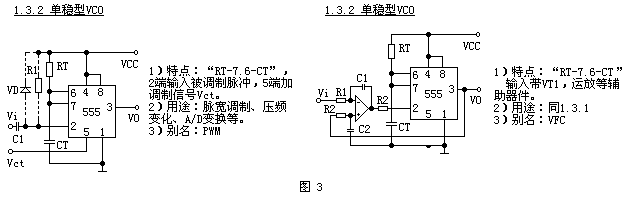
The third type (Fig. 3) is a voltage controlled oscillator. There are many single-stable voltage-controlled oscillator circuits, which are complicated. For the sake of simplicity, we only divide it into 2 different units. The circuit without any auxiliary device is 1.3.1; the circuit using an auxiliary device such as a transistor or an operational amplifier is 1.3.2. The figure shows two common circuits.
The bistable circuit here we will summarize and summarize the working mode of the 555 bistable circuit. The 555 bistable circuit can be divided into two types.
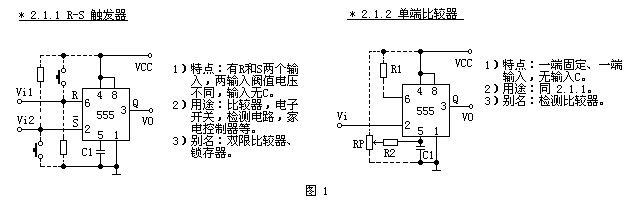
The first type (see Figure 1) is the trigger circuit with two units of double-ended input (2.1.1) and single-ended input (2.1.2). The single-ended comparator (2.1.2) can be 6-terminal fixed, 2-segment input; or 2-terminal fixed, 6-terminal input.
The second type (see Figure 2) is the Schmitt trigger circuit, which has the simplest form (2.2.1) and the input resistor adjusts the bias or adds the control voltage VCT at the control terminal (5) to change the threshold voltage ( 2.2.2) A total of 2 unit circuits.
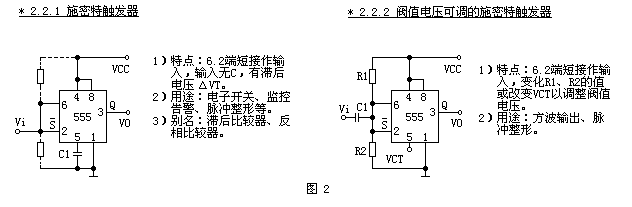
The input voltage terminal at the input of the bistable circuit generally has no timing resistor and timing capacitor. This is the structural feature of the bistable working mode. 2.2.2 C1 in the unit circuit only acts as a coupling, and R1 and R2 act as a DC bias.
The third category of unstable circuits is the unstable operation mode. The unstable circuit is a multi-resonant circuit, which is the most widely used type of 555 circuit. The circuit has the most variations. For the sake of simplicity, it is also divided into three types.
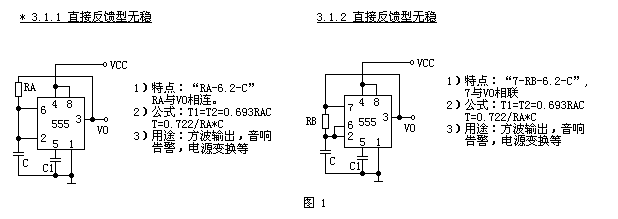
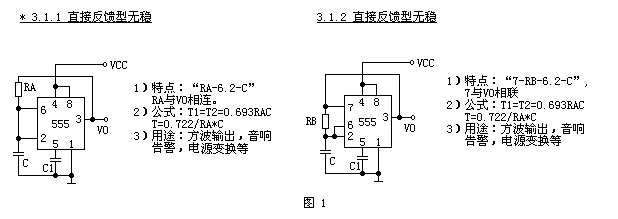
The first type (see Figure 1) is a direct feedback type with an oscillating resistor connected to the output VO.
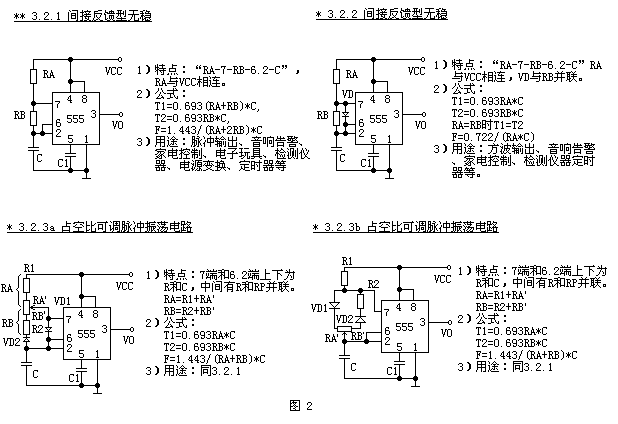
The second type (see Figure 2) is an indirect feedback type, and the oscillating resistor is connected to the power supply VCC. The first unit circuit (3.2.1) is the most widely used. The second unit circuit (3.2.2) is a square wave oscillation circuit. The third and fourth unit circuits are pulse oscillating circuits with adjustable duty cycles. The functions are the same and the circuit structure is slightly different. Therefore, the codes of 3.2.3a and 3.2.3b are respectively used.
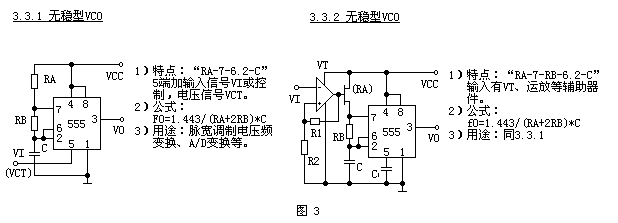
The third (see Figure 3) is a voltage controlled oscillator. Due to the complexity of the circuit variations, for the sake of simplicity, only the simplest form (3.3.1) and the two elements with the auxiliary device (3.3.2) are divided. The figure shows two application examples.
The input of the unstable circuit generally has two oscillating resistors and one oscillating capacitor. Only one oscillating resistor can be considered as a special case. For example: 3.1.2 units can be considered as the result of omitting RA. Sometimes it will encounter 7.6.2 three-terminal parallel connection, only one resistor RA unstable circuit, then it can be regarded as the 3.2.1 unit circuit to eliminate the deformation after RB.
The above summarizes the 555's 3 types and 8 kinds of 18 unit circuits. Although they are not possible to cover all 555 application circuits, the old saying goes: It is very helpful for us to understand most 555 circuits.
Pwm Solar Charge Controller ,Pwm Charge Controller,Go Power Solar Controller,Prostar 30 Solar Charge Controller
zhejiang ttn electric co.,ltd , https://www.ttnpower.com