Detailed antenna type
An antenna is a transducer that transforms a guided wave propagating on a transmission line into an electromagnetic wave propagating in an unbounded medium (usually free space), or vice versa. A component used in a radio device to transmit or receive electromagnetic waves. Engineering systems such as radiocommunication, broadcasting, television, radar, navigation, electronic countermeasures, remote sensing, radio astronomy, etc., all use electromagnetic waves to transmit information, relying on antennas to work. In addition, non-signal energy radiation also requires an antenna in terms of transmitting energy using electromagnetic waves. Generally, the antennas are reversible, that is, the same antenna can be used as both a transmitting antenna and a receiving antenna. The same characteristic parameters of the same antenna as transmitting or receiving are the same. This is the reciprocity theorem of the antenna.
Antenna functionThe antenna radiates radio waves and receives radio waves. However, the transmitter does not send radio waves through the feeder. The receiving antenna cannot send radio waves directly to the receiver via the feeder. The energy conversion process must pass. Below we take the radio communication equipment as an example to analyze the signal transmission process, and then explain the energy conversion effect of the antenna.
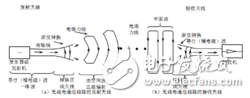
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of antenna energy conversion principle
At the transmitting end, the modulated high-frequency oscillating current (energy) generated by the transmitter is input to the transmitting antenna via the feeding device (the feeding device can directly transmit current waves or electromagnetic waves with different frequencies and forms), and the transmitting antenna will transmit high-frequency current Or the guided wave (energy) is converted into a radio wave—the free electromagnetic wave (energy) radiates to the surrounding space (see Fig. 1); at the receiving end, the radio wave (energy) is converted into a high-frequency current or a guided wave (energy) through the receiving antenna. The feeding device is transmitted to the receiver. It can be seen from the above process that the antenna is not only a device for radiating and receiving radio waves, but also an energy converter, which is an interface device between the circuit and the space.
working principleWhen a high-frequency current is applied to the conductor, an electric field and a magnetic field are generated in the space around it. According to the distribution characteristics of electromagnetic field in space, it can be divided into near zone, middle zone and far zone. Let R be the distance of the space from the conductor, at
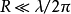
The time zone is called the near zone, and the electromagnetic field in this zone is closely related to the current and voltage in the conductor.
in
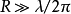
The area is called the far area, in which the electromagnetic field can leave the conductor and propagate to the space. Its change is delayed by a period of time relative to the current and voltage on the conductor. At this time, the electromagnetic wave propagated out is no longer with the current and voltage on the wire. There is a direct connection, and the electromagnetic field in this area is called the radiation field.
It must be pointed out that when the length L of the wire is much smaller than the wavelength λ, the radiation is very

antenna
Figure 2 antenna
Weak; the length L of the wire is increased to match the wavelength, and the current on the wire is greatly increased, so that stronger radiation can be formed.
The transmitting antenna utilizes this property of the radiation field so that the transmitted signal can be sufficiently radiated into space after passing through the transmitting antenna. How to make the conductor an effective radiation guidance system? Here we first analyze the situation on the transmission line. In the parallel two-line transmission line, in order to make only the energy transmission without radiation, it is necessary to ensure that the two-wire structure is symmetrical, the corresponding point current on the line is opposite in magnitude and direction, and the distance between the two lines "Ï€. In order for the electromagnetic field to radiate effectively, it is necessary to destroy the symmetry of the transmission line. For example, by separating the two conductors at a certain angle or removing one of them, the symmetry of the conductor can be destroyed to generate radiation.
As shown in Figure TX, the open-circuit transmission or the conductor at the terminal π/4 is separated in a straight line. At this time, the current on the terminal conductor is not in the opposite phase but in phase, so that the radiation field of the segment conductor at the space point. In-phase superposition constitutes an effective radiation system. This is the simplest and most basic unit antenna, called a half-wave symmetric vibrator antenna, with a characteristic impedance of 75Ω. After the electromagnetic wave is radiated from the transmitting antenna, it propagates to all sides. If a symmetric vibrator is placed in the direction of electromagnetic wave propagation, an induced electromotive force is generated on the antenna vibrator under the action of electromagnetic waves. When the antenna is connected to the receiving device, a high-frequency current is generated at the input of the receiving device. In this way, the antenna acts as a receiving device and converts the electromagnetic wave into a high-frequency current. That is to say, the antenna acts as a receiving antenna, and the receiving effect depends on the directionality and half-symmetry of the antenna in addition to the strength of the wave. Match the vibrator to the receiving device.
Antenna classification1. According to the nature of work, it can be divided into transmitting antenna and receiving antenna.
2, according to the use can be divided into communication antennas, broadcast antennas, TV antennas, radar antennas and so on.
3. According to the directionality, it can be divided into an omnidirectional antenna and a directional antenna.
4. According to the working wavelength, it can be divided into ultra long wave antenna, long wave antenna, medium wave antenna, short wave antenna, ultra short wave antenna, microwave antenna and so on.

Microwave antenna
Figure 3 microwave antenna
5, according to the structure and working principle can be divided into line antennas and surface antennas. The characteristic parameters describing the antenna are direction pattern, directivity coefficient, gain, input impedance, radiation efficiency, polarization and bandwidth.
6, according to the dimension can be divided into two types: one-dimensional antenna and two-dimensional antenna
One-dimensional antenna: It consists of a number of wires, either straight lines like those used on mobile phones, or some dexterous shapes, like the old bunny ears used on televisions before cables appear. Unipolar and dipole antennas are the two most basic one-dimensional antennas.
Two-dimensional antennas vary widely, with sheets (a square metal), arrays (a bundle of well-organized two-dimensional patterns), flared, and dished.
7, the antenna can be divided into three categories according to the use of the occasion: handheld antenna, vehicle antenna, base antenna.
Handheld antenna: It is the antenna for personal use of the walkie-talkie. There are two types of rubber antennas and whip antennas.
Car antenna: refers to the original design of the communication antenna installed on the vehicle, the most common application is the most popular

Disk antenna. The vehicle antenna structure also has an antenna in the form of a shortened type, a quarter-wavelength, a centrally-sensed type, a five-eighth wavelength, and a double-half wavelength.
Base station antenna: It plays a very important role in the entire communication system, especially as a communication station for communication hubs. Commonly used base station antennas are FRP high-gain antennas, four-ring array antennas (eight-ring array antennas), and directional antennas.
The Screen Protector has a self-healing technology that can automatically eliminate small scratches on the Protective Film within 24 hours. Significantly reduce dust, oil stains and fingerprint smudges, anti-scratch.
The Screen Protection Film is very suitable for curved or flat screens. The Soft Hydrogel Film perfectly matches the contour of your device. Will not affect any functions of the phone.
The Ultra-Thin Protective Film with a thickness of only 0.14mm uses 100% touch screen adaptive screen touch screen technology, complete touch screen response, high-tech technology makes the screen touch to achieve zero delay, ultra-thin material brings you "realism".
The Protection Film has excellent clarity and incredible toughness, providing a high level of clarity and a glass-like surface, highlighting the sharpness of the most advanced smartphone display images and bright colors.
If you want to know more about Self Repair Screen Protector products, please click the product details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Self Repair Screen Protector.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about the Self Repair Screen Protector!
Self-healing Protective Film, Self-repairing Screen Protector,Self-healing Screen Protector, Self-Healing Hydrogel Film,Hydrogel Film Screen Protector
Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.mct-sz.com