Experience sharing of experimental circuits with breadboards
     Several options for preparing the experiment board are described above. Here I will introduce the first option. I will build a simple single-chip experimental board together with everyone to experience the fun of hands-on practice.
We have two ways to build a test board ourselves, one is to use breadboards, and the other is to use universal welding plates. In this article we introduce the breadboard construction circuit.
The breadboard is a device used in circuit experiments with a lot of holes. We can insert components and wires into the circuit we need. If the circuit is found to be faulty, unplug the component and rewire the cable. After the circuit is finished, all components can be unplugged and used again.
Breadboard construction is simple and easy, saving time and materials. However, the disadvantage is that the breadboard can only be used to build some relatively simple circuits, and it is a circuit that does not require high electrical connections. If the circuit is too complicated, the breadboard is full of various wires, and some wires or components are loose, which is not easy to find; if some circuits have higher requirements for electrical connection, such as passing a large current, weak signal processing, high Frequency circuits, etc., because the components are simply inserted, and the resistance value between the board and the breadboard is large, the effect is not satisfactory.
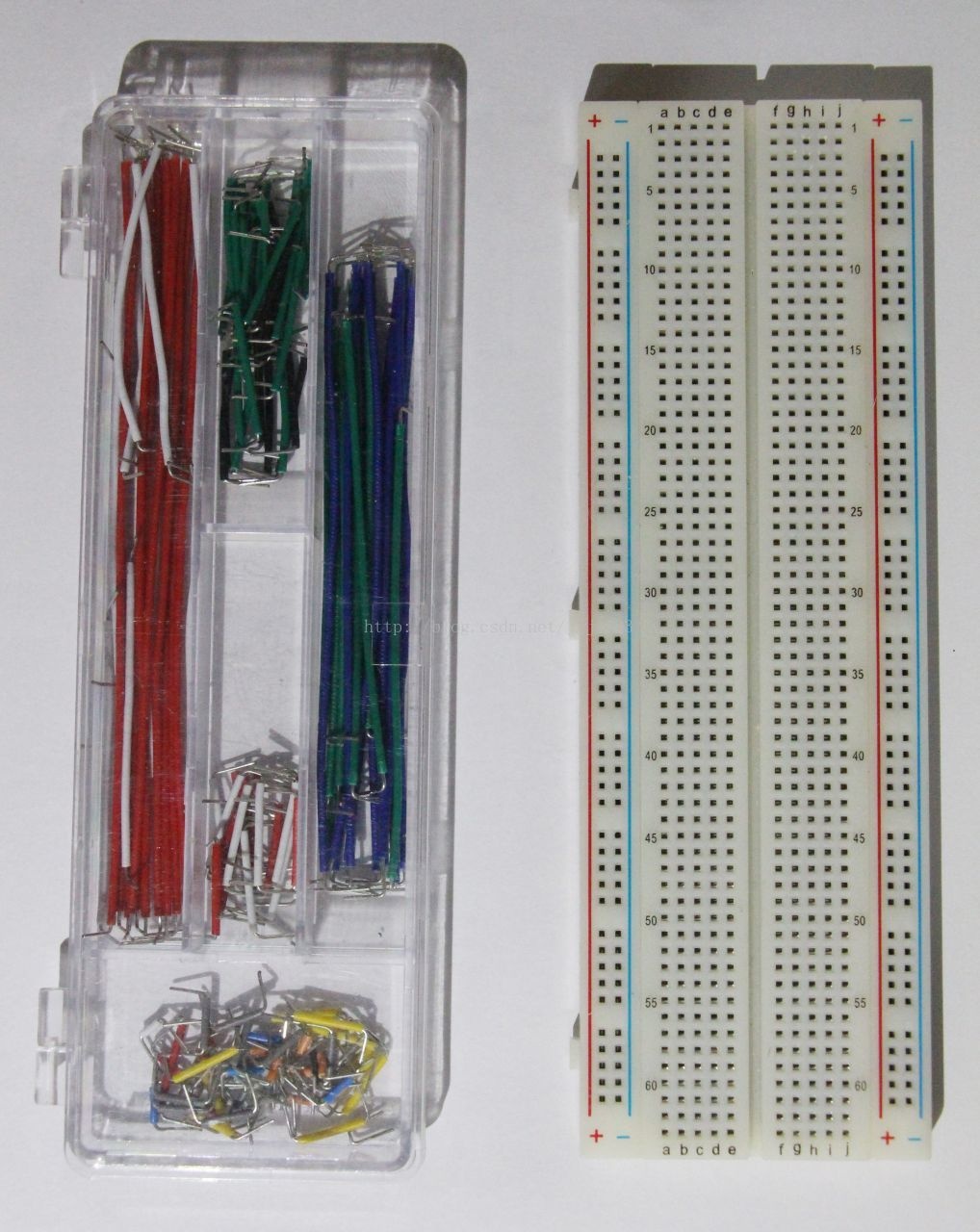
The figure below shows the breadboard line and a common breadboard. The breadboard line can be made of a normal hard wire of suitable thickness or a dedicated wire as shown in the figure, which is more convenient.
The breadboard in the figure, the entire vertical row marked with red and blue lines on the outside is connected together, and is generally used for power supply. Each of the five horizontal holes in the middle is connected together for plugging various components.
Turn to the topic below, build a simple single-chip experimental board. The minimum circuit of the single-chip microcomputer is the minimum circuit of the normal operation of the single-chip microcomputer. Here we must start from the minimum system. The following tool materials are required:
Breadboard, breadboard line, wire, DuPont line
STC89C52RC microcontroller in DIP40 package (STC89C5x can be used)
11.0592MHz crystal oscillator, 30pF capacitor two (for clock circuit)
10uF capacitor, 10k resistor (for reset circuit)
USB-TTL download line (for program burning, will be described in detail later)
Six-legged self-locking switch (as a power switch, can be omitted, and replaced by a plug wire)
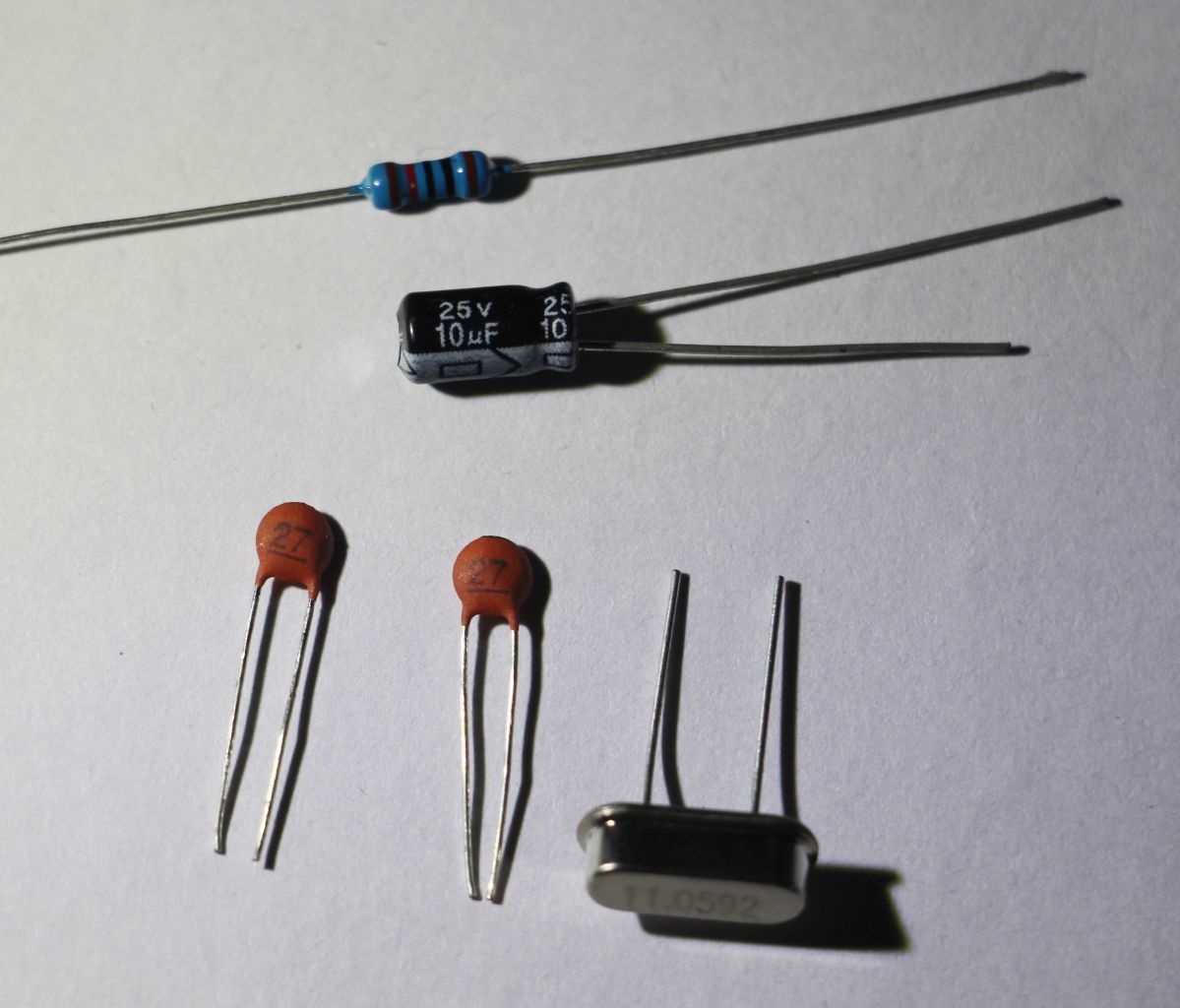
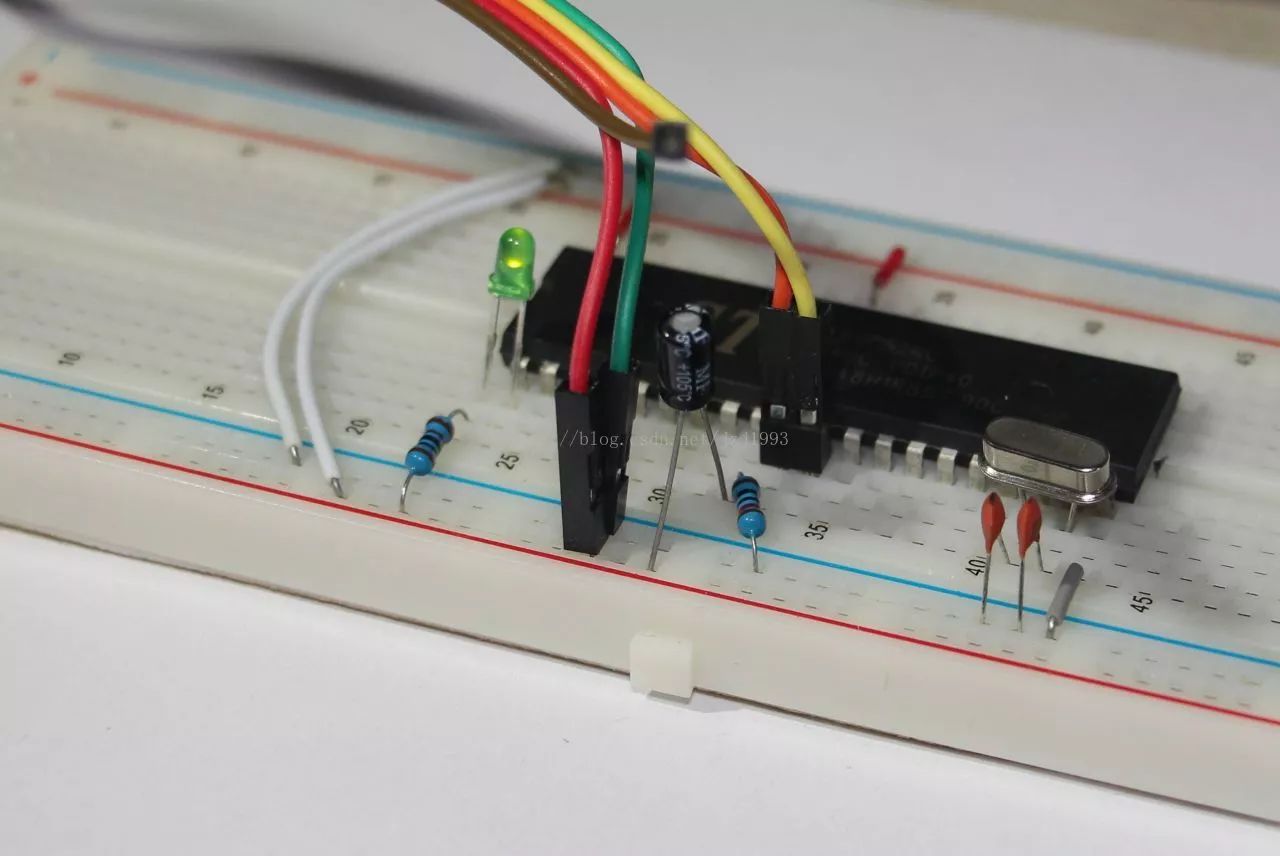
The components in the figure are used for the reset circuit and the clock circuit. The above is a 10k color ring resistor, please read it yourself. Then there is a 10uF point solution capacitor. The electrolytic capacitor has positive and negative poles. The pin on the skin with the white arrow on the skin is the negative pole. If it is as shown in the figure, it is brand new. Electrolytic capacitor, the positive pin is longer; below the left is two ceramic capacitors, I did not find 30pF I used the relatively close 27pF instead, the specific capacity reading also please learn by yourself; the lower right corner is the crystal, the front is marked 11.0592, ie The crystal has a frequency of 11.0592 MHz.
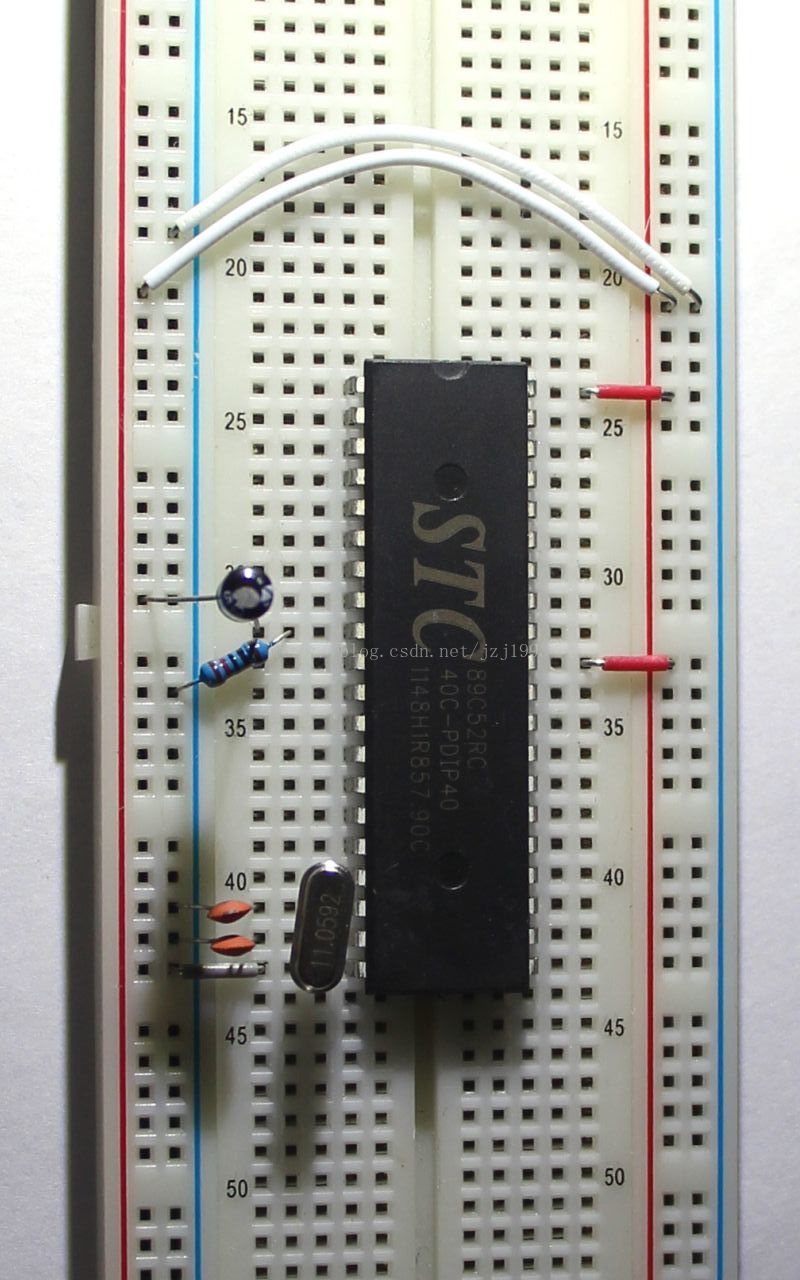
In the figure is the minimum system built, two white lines are used to connect the positive and negative sides of the two sides together.
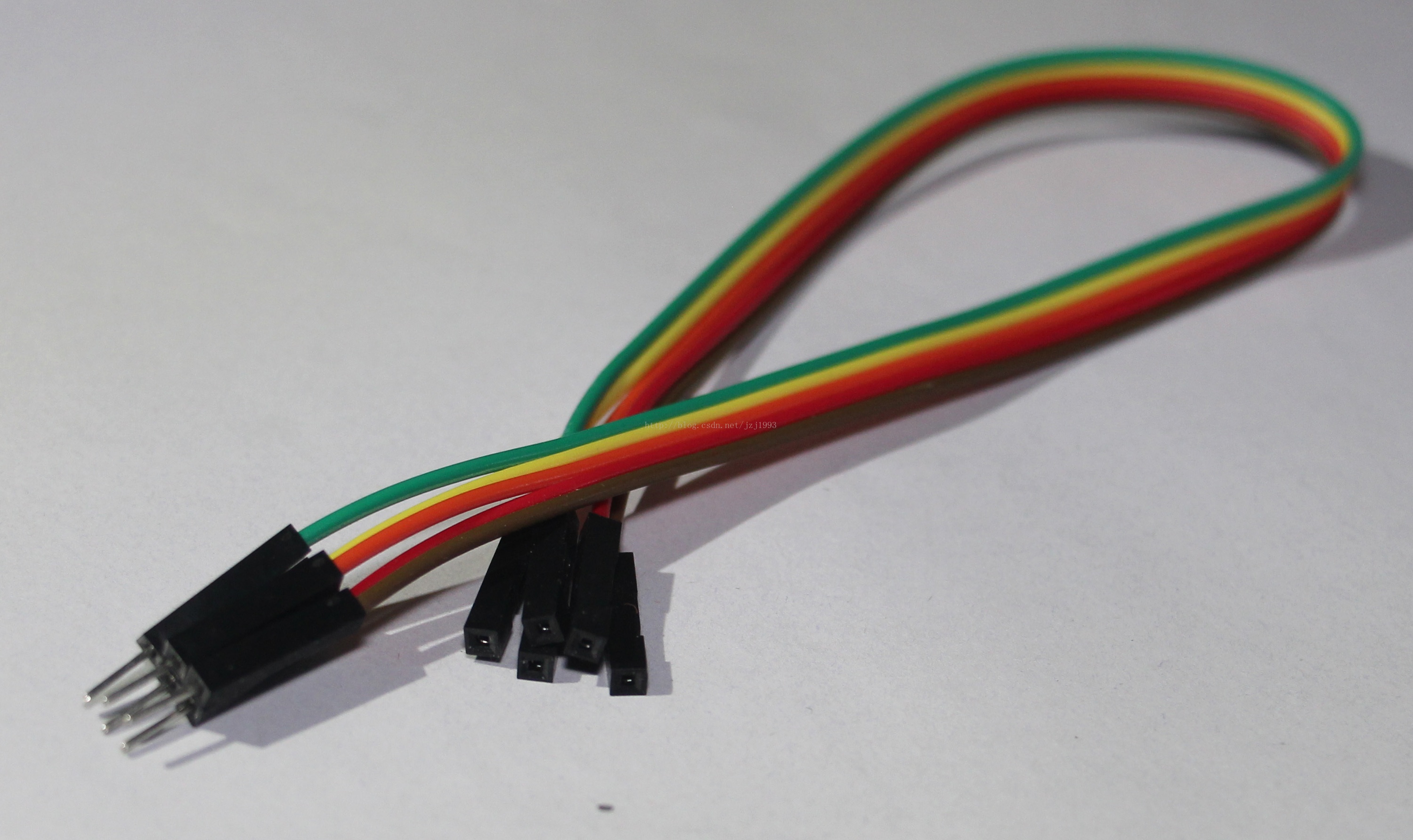
DuPont line with male end (pin) and female end (jack) at one end
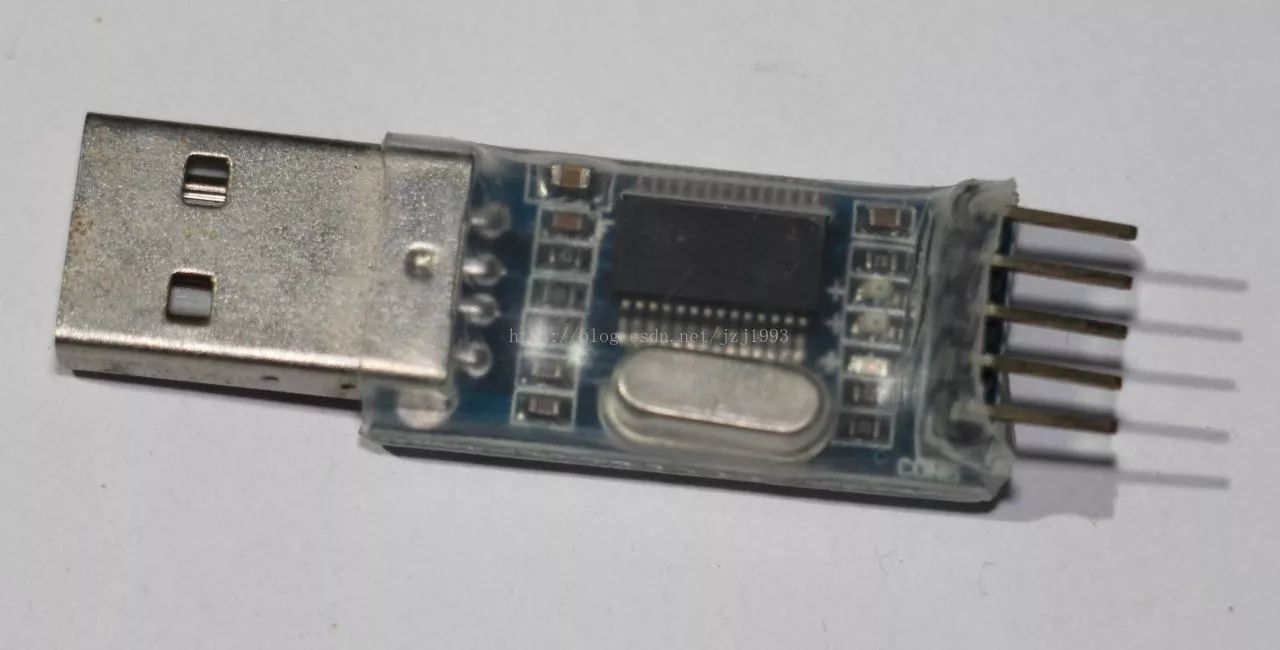

USB-TTL adapter board front
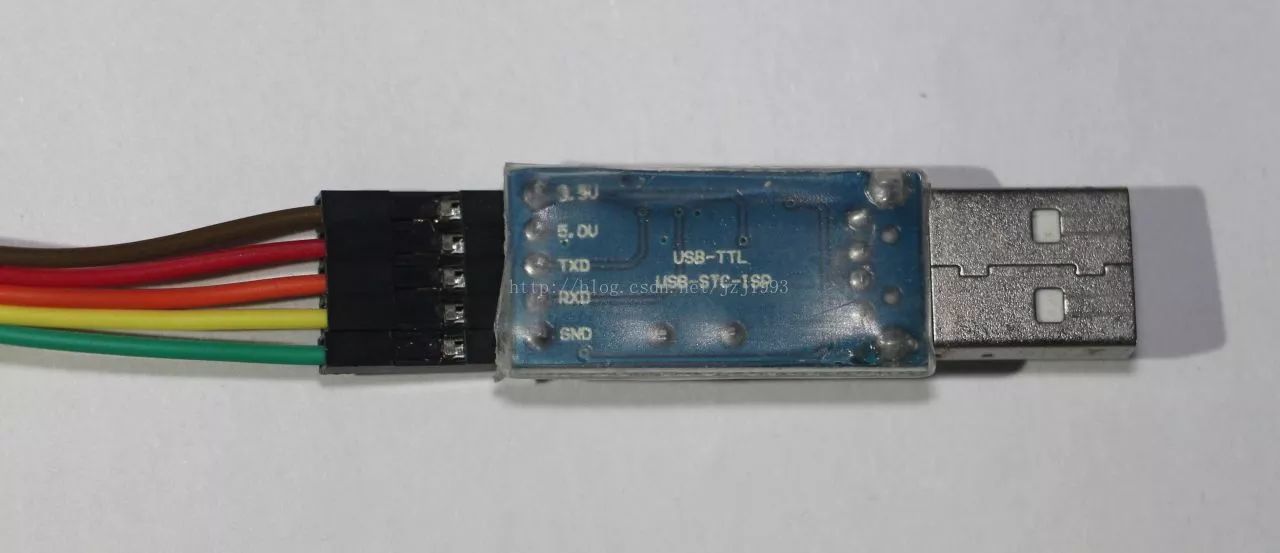
The reverse side of the USB-TTL adapter board (connected to the DuPont line female)
The DuPont line female head is connected with a USB-TTL adapter board (hereinafter referred to as the adapter board), and the male end of the DuPont line is inserted on the breadboard and connected to the minimum system of the single chip microcomputer. 5V connected to the breadboard on the adapter board (my adapter board has 5V and 3.3V two supply voltages, some adapter boards only have one VCC, then connect to VCC), GND connects the negative board of the breadboard, that is, the microcontroller GND, the two wires can supply power to the MCU; the TXD on the adapter board is connected to the RXD (P3.0) of the MCU, and the RXD is connected to the TXD (P3.1) of the MCU (refer to the 51 MCU pin distribution diagram introduced earlier) These two lines are used for serial communication and download procedures, which will be described in detail later.
In the figure, I have connected the circuit, and I connected an LED and a resistor to the P1.0, and downloaded the LED flashing program with the computer. You can see that the green LED is lit in the photo.
Tubular Stranding Machine
Tubular and planetary stranding machines for production of steel wire ropes.
Tubular rotor supported by bearing, bearing lubrication by centralized circulating oil.
Planetary cages supported by bearing or under roller, with back twist.
Lay length optional by gearbox or by electrical system.
Machine design customized.
Tubular Strander,Stranding Machine,Wire Stranding Machine,Tubular Stranding Machine
ROYAL RANGE INTERNATIONAL TRADING CO., LTD , https://www.royalrangelgs.com