Electrical instrumentation_Electrical common instrumentation_Multi-function electric instrument brand
Various AC and DC current meters, voltmeters, power meters; electricity meters, phase meters, power factor meters, multimeters, insulation resistance meters, grounding resistance meters, clamp meters, single and double bridges, resistance boxes, electrostatic voltmeters, etc. It is a common instrument used by electricians. Do you know the characteristics and brand of these instruments? The following small series searched the network for some relevant information for your electrician friends to refer to.

1. Electrician measuring instrument
2. Electrical measurement indicating instrumentation
3. Electrical measurement digital instrumentation
4. Electrical measurement recording instrumentation (including statistical voltmeter)
5. Electric energy meter (including maximum demand electric energy meter, time-sharing electric energy meter, multi-rate electric energy meter, multiple
Functional energy meter, standard energy meter, etc.)
6. Energy metering device (including power load monitoring device)
7. Current and voltage transformers (including measuring transformers, standard transformers, calibrators and load boxes). Transform instrumentation (including power transmitter, AC sampling and measuring device)
9. Electrical measurement system secondary circuit (including PT secondary circuit pressure drop test device)
10. Electrical measurement standard device
11. Energy metering and billing system
12. Electrical test instruments (including relay protection testers, high-voltage measurement test equipment, etc.)
Electrician commonly used instrumentation1, ammeter
The ammeter (Figure 1) is divided into DC current meter and AC current meter. When using the ammeter, be careful to select the correct range. It should be connected in series to the actual circuit being measured. The current of the ammeter flows from the "+" polarity end of the meter, and the "one" polarity end flows out. When wiring, it should be done under power failure. DC ammeters are not allowed to be used on AC circuits.

Figure 1 ammeter
2, clamp ammeter
Clamp-type ammeters are also known as card meters (Figure 2). Commonly used are AC clamp-type ammeters and AC-DC clamp-type ammeters. When using, pay attention to the voltage level of the meter and the voltage level of the measured line or equipment. Set the range block to be greater than or equal to the measured current value. Before measuring, estimate the current or voltage to be measured, or compare it first. The large range then looks at the size of the measured value to change the range. Note that the jaws must be opened when switching the range. When there is no power, it is not allowed to switch the range with power. When measuring, place the wire to be tested in the center of the jaw and the jaw should be closed.
When using, pay attention to keep a sufficient distance from the charged body and have someone to monitor. Never use a clamp meter to measure bare conductors, nor use them in a three-phase knife switch or fuse.
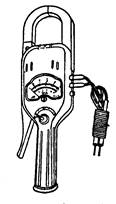
Figure 2 clamp current meter
3, voltmeter
The voltmeter (Figure 3) is divided into two types: DC voltmeter and AC voltmeter. When using the voltmeter, pay attention to selecting the correct range. It should be connected in parallel at both ends of the line to be measured, and then wired according to the “+†and “one†polarity marks on the voltmeter terminal.
When wiring, it should be done under power failure. It is not allowed to use the voltmeter in series in the circuit being measured.

Figure 3 voltmeter
4, the multimeter
Multimeters are also called multimeters (Figure 4). A general multimeter can be used to measure DC current, AC current, DC voltage, AC voltage, resistance, capacitance, transistor parameters and audio level. There are two types of digital and mechanical (or electronic) multimeters. Pay attention to zero calibration before each measurement. When using, pay special attention to the shift and the measured range.

Figure 4 Multimeter
5, insulation resistance meter
The insulation resistance meter, also known as the megohmmeter and the shaker (Fig. 5), has both a hand-cranked generator and a transistor. When measuring, do not make the measurement range excessively exceed the value of the insulation resistance to be tested, so as to avoid large errors in reading. When using, the power of the device under test must be cut off, and the device should be short-circuited to the ground, so that the device is completely unpowered to ensure personal and equipment safety.
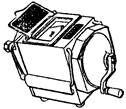
Figure 5 insulation resistance meter
6, electric energy meter (commonly known as electricity meter)
The electric energy meter (Fig. 6) mainly measures the electric energy used for a certain period of time. There are two types of active energy meter and reactive energy meter.
The active energy meter can be further divided into a single-phase electric energy meter and a three-phase electric energy meter. When using, pay special attention to the electric energy meter with the specifications corresponding to the rated voltage and rated current of the circuit under test. At the same time, pay attention to the correct wiring according to the nameplate on the energy meter.

Figure 6 Energy meter
What are the brands of electric multi-function instrumentation companies?The following are ten domestic multi-function instrument brands that have been compiled from the Internet and are available for reference by electricians.
Xi'an Wesson Electric Co., Ltd.
Shennian Power Technology Co., Ltd.
Fuling Aobosen Electric Factory
Nanjing Nengbao Electric Co., Ltd.
Zhuhai Snowova Technology Co., Ltd.
Suzhou Langlis Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
Changzhou Sanhe Sound Source Ultrasonic Technology Co., Ltd.
First planning company
Jiangsu Ankerui Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Shenzhen Guodian Xuzhen Electric Technology Co., Ltd.
Electrical instrument accuracy level1 . Instrument error
The error of the meter refers to the difference between the indicated value of the meter and the measured true value. It has three representations: (1) absolute error; (2) relative error; and (3) reference error.
The error of the meter is divided into two parts: basic error and additional error. The basic error is caused by the characteristics of the instrument itself and the manufacturing and assembly defects. The basic error is expressed by the reference error of the instrument. The additional error is caused by external factors such as external temperature, external incoming magnetic field, and instrument working position.
2 . Meter accuracy level
There are 7 meter accuracy levels, see the table below.

Table accuracy level
Usually 0.1 and 0.2 gauges are standard gauges; grades 0.5 to 1.0 are for laboratories; grades 1.5 to 5.0 are for electrical engineering surveys. The accuracy of the measurement is not only related to the accuracy level of the meter, but also to its range. Therefore, the range should always be as large as 2/3 of the full scale when selecting the range. The multimeter is a multi-functional, multi-range portable electric instrument. The general multimeter can measure DC current, DC voltage, AC voltage and resistance. Some multimeters can also measure capacitance, power, transistor common-emitter DC amplification factor hfE, and so on. Therefore, the multimeter is one of the necessary instruments for electricians. Multimeters can be divided into pointer multimeters and digital multimeters.
Diesel generator assembly by diesel engine, alternator, radiator, controller, base frame;
. World famous diesel engine brand: Cummins, Perkins, MTU, Kubota, Yuchai, Mitsubishi, Deutz, Doosan, MWM, GE, CRRC, Etc
. World famous AC alternator brand: Stamford, Leroy Somer, Mecc Alte, Marathon, Faraday, SWT
. World famous genset controller brand: Deepsea, ComAp, Deif, SmartGen,
. Good Quality Cooling Radiator
. Start Battery System
. Fuel Supplying System
. Filtering System
. Intake and Exhaust System
Diesel Genset,Diesel Generator,Diesel Generator Set,Portable Diesel Generator
Guangdong Superwatt Power Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.swtgenset.com