Brief Introduction of Power Industry Operation in the First Half of 2013
 In the first half of the year (June-June), the nation’s electricity supply and demand remained in balance as a whole, and the nation’s electricity market continued to grow at a moderate rate since last year. The growth rate fell slightly from the same period of last year; hydropower generation maintained double-digit growth year-on-year. The utilization hours of hydropower increased more, thermal power generation volume grew at a low rate, and the number of hours of utilization of thermal power provinces decreased year-on-year. The investment in power grid projects completed a rapid year-on-year increase, and power supply investment decreased slightly year-on-year, with nuclear power investment decelerating significantly year-on-year. The newly-added power generation capacity of infrastructure increased by more than 20% compared with the same period of last year, and the scale of thermal power construction under construction was significantly reduced year-on-year. The electricity sent by provinces across the country has maintained steady growth.
In the first half of the year (June-June), the nation’s electricity supply and demand remained in balance as a whole, and the nation’s electricity market continued to grow at a moderate rate since last year. The growth rate fell slightly from the same period of last year; hydropower generation maintained double-digit growth year-on-year. The utilization hours of hydropower increased more, thermal power generation volume grew at a low rate, and the number of hours of utilization of thermal power provinces decreased year-on-year. The investment in power grid projects completed a rapid year-on-year increase, and power supply investment decreased slightly year-on-year, with nuclear power investment decelerating significantly year-on-year. The newly-added power generation capacity of infrastructure increased by more than 20% compared with the same period of last year, and the scale of thermal power construction under construction was significantly reduced year-on-year. The electricity sent by provinces across the country has maintained steady growth. In June, the growth rate of electricity consumption in the society as a whole rose slightly from last month. The growth rate of electricity consumption of urban and rural residents increased significantly year-on-year and month-on-month; the electricity consumption of the manufacturing industry increased slightly year-on-year, and the electricity consumption of the four high-energy-consuming industries increased. The year-on-year growth rate of the growth rate has dropped from last month. The year-on-year growth rate of hydropower generation dropped sharply from the same period of last year; the nationwide electricity transmission across the region increased rapidly year-on-year, and the southwestern power grid had a negative year-on-year growth in electricity from west to east, but the electricity volume still increased more than last month.
First, the growth rate of electricity consumption of urban and rural residents in June was significantly increased
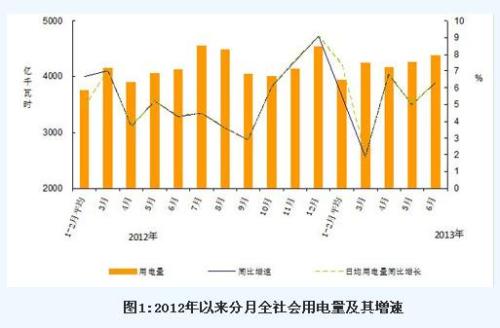
In the first six months of the year, the country’s entire society used 248.15 billion kWh of electricity, an increase of 5.1% year-on-year, 0.4% lower than the same period of last year.
In terms of sub-sectors, from January to June, the primary industry used electricity of 46.1 billion kwh, which was a year-on-year decrease of 0.8%, accounting for 1.8% of the total electricity consumption of the society; secondary industry electricity consumption was 1841.9 billion kwh, a year-on-year increase. 4.9%, accounting for 73.8% of the total social power consumption, contributed 70.3% to the growth of electricity consumption in the entire society, and the tertiary industry used 292.5 billion kWh, an increase of 9.3% over the same period of the previous year, accounting for electricity consumption in the entire society. The proportion of volume was 11.7%; the urban and rural residents’ electricity consumption was 315.6 billion kWh, an increase of 3.9% year-on-year, 8.8 percentage points lower than the same period of last year, and electricity consumption accounted for 12.6% of the total electricity consumption of the society. The contribution rate of electricity consumption growth in the entire society was 9.7%.
In terms of regions, from January to June, there were 16 provinces where the growth rate of electricity consumption in the whole society was higher than the national average (5.1%), of which the provinces with a growth rate higher than 10% were: Xinjiang (31.1%) and Yunnan ( 13.1%), Qinghai (11.3%) and Hainan (10.9%); the province with the lowest growth rate of electricity consumption in the whole society is Shanghai (0.2%).
In June, the country’s entire society used 448.4 billion kWh of electricity, an increase of 6.3% year-on-year, an increase of 1.3 percentage points from the previous month. In terms of sub-industries, the primary industry used 9.9 billion kWh, a year-on-year decrease of 7.1%; the secondary industry used 331.6 billion kWh, an increase of 5.7% year-on-year, and contributed 69.2% to the growth in electricity consumption of the entire society; The electricity consumption of the tertiary industry was 49.8 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 10.5%, and the contribution rate to the growth of electricity consumption of the entire society was 18.3%. The electricity consumption of urban and rural residents was 47 billion kWh, an increase of 9.3% year-on-year, and the growth rate was yoy. It rose 4.0 and 5.0 percentage points month-on-month and contributed 15.4% to the growth of electricity consumption in the entire society.
In terms of regions, in June, there were 14 provinces where the growth rate of electricity consumption in the whole society was higher than the national average (6.3%), of which the provinces with a growth rate higher than 10% were Xinjiang (33.7%) and Yunnan (20.0%). ), Chongqing (15.9%), Hainan (15.4%), Jiangxi (14.1%), Zhejiang (11.1%), and Fujian (10.2%); Provinces where the growth rate of electricity consumption in the whole society is negative: Shanxi (-2.7%) ) and Heilongjiang (-0.3%).
Second, the average daily electricity consumption in the manufacturing industry in June
From January to June, the national industrial electricity consumption was 1810.8 billion kWh, an increase of 4.8% year-on-year, an increase of 1.1 percentage points over the same period of the previous year, and electricity consumption accounted for 72.5% of the total electricity consumption of the entire society. The contribution rate of electricity growth is 68.3%. Among them, light and heavy industrial power consumption were 300.5 billion kWh and 151.30 billion kWh, respectively, an increase of 4.9% and 4.8% year-on-year, respectively, an increase of 1.1 and 1.2 percentage points over the same period of last year.
In June, the country’s industrial electricity consumption was 326.3 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 5.7%, and its contribution to the growth of electricity consumption in the entire society was 67.6%. Among them, electricity consumption for light and heavy industries was 5,9 billion kWh and 270.5 billion kWh respectively, which was a year-on-year increase of 4.3% and 6.0% respectively, which was a decrease of 2.4 and a 3.4 percentage point increase over the same period of the previous year.
From January to June, the country’s electricity consumption in the manufacturing industry was 1341.2 billion kWh, an increase of 4.8% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 2.3% higher than the same period of last year. In June, the country’s electricity consumption in the manufacturing industry totaled 242.8 billion kWh, up 4.3% year-on-year, 1.0 percentage points lower than that in May; the average daily electricity consumption of the nation’s manufacturing industry was 8.1 billion kWh/day, an increase of 390 million from the previous month. In kilowatt-hours/day, the monthly average daily electricity consumption of the manufacturing industry hit a new high.
3. The growth rate of the total electricity consumption of the four high-energy-carrying industries in June was slightly lower than that of the previous month.
From January to June, the total electricity consumption of the four high-energy-consumption industries including chemical raw material products, non-metallic mineral products, ferrous metal smelting, and non-ferrous metal smelting totaled 789.8 billion kwh, an increase of 4.2% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 1.6 more than the same period of last year. In percentage points, electricity consumption accounted for 31.6% of the total electricity consumption in the society, and contribution rate to the growth of electricity consumption in the whole society was 26.0%, which was 11.1 percentage points higher than the same period of last year. Among them, the chemical industry used 190 billion kwh electricity, an increase of 4.4%; building materials industry electricity consumption 142.7 billion kwh, an increase of 3.1%; ferrous metal smelting industry electricity consumption 263.3 billion kwh, an increase of 3.5%; The metal smelting industry was 193.7 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 5.7%. The growth rates of electricity consumption in the building materials and steel industries increased by 4.0 and 7.5 percentage points over the same period of the previous year, and the growth rate of electricity use in the chemical and non-ferrous industry fell by 2.3 and 1.4 percentage points respectively.
In June, the four high-energy-consumption industries used a total of 140.8 billion kwh of electricity, an increase of 2.5% year-on-year, and the growth rate fell by 0.6% from the previous month. Among them, the electricity consumption of the chemical industry was 33.3 billion kWh, an increase of 4.1% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 2.2 percentage points higher than the previous month; the electricity consumption of the building materials industry was 28.6 billion kWh, an increase of 5.8% year-on-year, and the growth rate fell by 1.3 from the previous month. The percentage of electricity consumption in the ferrous metal smelting industry was 45.8 billion kWh, down 0.3% year-on-year, and the growth rate was down 2.7 percentage points from the previous month. Non-ferrous metal smelting industry was 33.2 billion kWh, up 2.3% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 0.2% higher than the previous month. Percentage.
Fourth, June hydroelectric power generation growth slowed compared to the same period last year
According to statistics from the National Bureau of Statistics, in the first six months of the year, the total output of power plants above designated size was 2,344.2 billion kWh, an increase of 4.4% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 0.7 percentage points higher than the same period of last year. In June, the generating capacity of power plants above designated size nationwide was 425.3 billion kWh, an increase of 6.0% year-on-year.
From January to June, the hydropower generation capacity of power plants above the designated size of the country was 329 billion kWh, an increase of 11.8% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 1.9 percentage points higher than that of the same period of last year. Among them, the hydropower generation in June was 81.5 billion kWh, an increase of 5.7% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 13.7 percentage points lower than the same period of the previous year. In terms of provinces, of the 12 provinces with more hydropower (more than 5 million kilowatts), The fastest-growing is Yunnan (33.5%), followed by Sichuan (13.8%), and the larger declines are Guangxi (-28.7%) and Guizhou (-10.6%). The three provinces with the largest hydropower generation are Sichuan (15.9 billion kWh), Hubei (13.2 billion kWh) and Yunnan (11.4 billion kWh), and the combined hydropower generation accounts for 50% of the country’s total hydropower generation.
From January to June, thermal power generation capacity of power plants above designated size nationwide was 195 billion kWh, an increase of 2.6% year-on-year; in June, thermal power generation capacity was 324 billion kWh, an increase of 4.9% year-on-year.
From January to June, the national nuclear power generation capacity was 47.7 billion kWh, an increase of 3.0% year-on-year; the power generation of wind farms of 6000 kW and above was 70.2 billion kWh, an increase of 39.3% year-on-year.
V. The utilization hours of wind power equipment increased more than the same period of last year
From January to June, the cumulative average utilization hours of power generation equipment in the country was 2,173 hours, which was a decrease of 64 hours compared with the same period of the previous year, and the decrease was more than 8 hours from January to May.
In terms of types, from January to June, the average utilization hours of hydropower equipment nationwide was 1,532 hours, an increase of 76 hours over the same period of the previous year. Among the 7 provinces with the largest hydropower installed capacity, Guangxi increased 357 hours year on year, Guizhou increased 319 hours, and Qinghai increased. 250 hours, Yunnan increased 208 hours; Hubei decreased 207 hours. The average utilization hours of thermal power equipment in the country was 2412 hours, which was 83 hours lower than the same period of the previous year. The number of thermal equipment utilization hours in the 10 largest thermal power provinces with installed thermal power capacity of more than 30 million kilowatts decreased compared with the same period, and the most significant declines were as follows: Guangdong (down 269 hours), Liaoning 218 (down 180 hours) and Henan (down 215 hours). The average utilization hours of nuclear power equipment nationwide was 3,543 hours, which was 195 hours lower than the same period of the previous year. The average utilization hours of wind power equipment nationwide was 1,011 hours, an increase of 91 hours over the same period of the previous year. In terms of provinces, Sichuan Province (1,825 hours), Yunnan (1594), and Shanxi (1510) were the provinces with high wind turbine utilization hours (more than 1,400 hours). Hours), Guangdong (1455 hours), Shaanxi (1442 hours), and Tianjin (1415 hours); in provinces with wind power installed capacity of more than 2 million kilowatts, except for Hebei, other provinces have increased their utilization hours, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Jilin Heilongjiang and Gansu were below the national average, especially Jilin and Gansu, with only 837 hours and 875 hours respectively.
Sixth, the national power transmission across provinces has grown steadily
From January to June, the nationwide trans-regional transmission of electricity reached 98.3 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 13.5%. Among them, North China sent Central China (UHV) to 7.2 billion kWh, down 0.7% year-on-year; North China sent 7.8 billion kWh to East China, down 9.8% year-on-year; Northeast China sent 6.3 billion kWh to North China, up 15.5% year-on-year; Central China sent East China to 26.6 billion. Kilowatt-hour, an increase of 96.0% over the same period of last year, mainly due to the significant increase in upward direct-current power transmission and Jinsu-Suzhou direct investment in the first half of the year. Central China sent south a total of 10.1 billion kwh, a year-on-year decrease of 15.4%; northwest China and North China sent a total of 23 billion kilowatt-hours. , a year-on-year decrease of 11.3%; Three Gorges Power Station delivered a total of 32.5 billion kWh of electricity, a year-on-year decrease of 5.6%.
From January to June, the provinces sent a total of 346.8 billion kWh of electricity, an increase of 10.1% year-on-year. China Southern Power Grid sent 54.8 billion kWh to West China, an increase of 31.7% year-on-year.
In June, the nationwide transmission of electricity across the region completed 19.3 billion kwh, an increase of 16.8% year-on-year; the Three Gorges sent out electricity of 8.5 billion kwh, a decrease of 0.4% year-on-year. The provinces sent a total of 65.7 billion kwh of electricity, an increase of 9.3% year-on-year. China Southern Power Grid sent 12.3 billion kWh of electricity to the east, a year-on-year decrease of 6.7%.
VII. The scale of newly installed infrastructure has rebounded, and the scale of thermal power construction continues to decline year-on-year
From January to June, the country’s newly-added power generation capacity for infrastructure construction was 32.43 million kilowatts, an increase of 6.58 million kilowatts over the same period of last year. Among them, hydropower was 8.89 million kilowatts, nuclear power was 2.21 million kilowatts, and solar power was 1.38 million kilowatts, which was 3.26 million kilowatts, 2.21 million kilowatts, and 1.23 million kilowatts more than the same period of last year. Thermal power, grid-connected wind power was 15.85 million kilowatts and 4.1 million. Kilowatts, basically the same as last year. In terms of provinces, the provinces with the most new power projects in the first half of the year were: Yunnan (3.67 million kilowatts, including 3.27 million kilowatts of hydropower), Jiangsu (3.5 million kilowatts, of which 3.36 million kilowatts of thermal power), and Sichuan (32.8 million kilowatts). Of which, 2.63 million kilowatts of hydropower) and Hebei (2.2 million kilowatts, of which 1.91 million kilowatts of thermal power).
From January to June, the new power projects for the major power generation enterprises across the country started a new scale of 17.28 million kilowatts. As of the end of June, the power project is under construction at a scale of about 160 million kilowatts.
From January to June, the capacity of new substations with 220 kilovolts and above was 106.27 million kVA, and the length of the lines was 20,491 kilometers, which was 6 million kVA and 3,942 kilometers more than the same period of last year.
Power Adapter,Universal Power Adapter,Usb Power Adapter,67W Usb-C Power Adapter
Guang Er Zhong(Zhaoqing)Electronics Co., Ltd , http://www.gezadapter.com