Research on the change of the proportional mixture after accessing the energy storage power station in the power grid
The energy storage power station mainly refers to an energy storage system composed of various types of energy storage methods, which can effectively realize demand side management, eliminate peak-to-valley difference, and smooth load. By adjusting the operation mode of the energy storage power station, the electric energy sent by the distributed power source is stored or regulated, and the distributed power source is connected to the power grid with high quality; or the energy storage power station system can be used to store electric energy when the power is sufficient, when the power is scarce Release electricity to resolve supply and demand conflicts.
The famous American scholar Jeremy Rifkin first proposed the vision of the energy Internet and attracted widespread attention at home and abroad. Energy Internet combines Internet technologies based on smart grids to change energy use patterns. Rifkin believes that supporting large-scale distributed generation systems and distributed energy storage systems is one of the biggest features of the energy Internet. The “out-of-the-box†operation mode of the traditional power system will be replaced by the “storage of energy storage and joint supply†mode, and the energy storage power station will be one of the most important technologies of the energy Internet. It can be foreseen that the current "out-of-the-box" operation mode of the power system will be replaced by the mode of "storage and energy supply joint supply and supply".
For a long time, the dynamic behavior analysis of the power grid is mostly realized by the “simulation-modeling-solution†method based on reduction theory. It is difficult to reasonably explain the internal mechanism of large-scale power outage accidents caused by small faults. Using complex network theory, through the analysis of the topology of the power grid, the fault propagation mechanism and critical dynamic behavior are studied, and then the system reconstruction is redesigned and optimized.
Traditional power system nodes can be divided into two types: power generation type and power receiving type. For example, a power station is a power generation type node, and a substation is a power receiving type node. However, after the energy storage system is added, the topology and function of the system will change accordingly. For example, in the case of energy storage type substation, it can be regarded as a power receiving type node, and when it is discharged, it can be regarded as a power generation type node.
The energy storage power station will have a direct effect and influence on the grid operation due to its “role-conversion†of “power generation-storageâ€, and the grid topology will inevitably change accordingly. Among them, the “role conversion†of energy storage power plants has the most direct impact on network proportionality. AssortaTIve Mixing, also known as proportionality, is a special feature of complex network topologies. A type of node with certain characteristics in the network tends to be connected to a node with the same characteristics, which is called symmetry (AssortaTIvity). If a node tends to connect to a node with a different feature, it is called DissorortaTIvity. .
For a long time, scholars have done a lot of work on the application planning of energy storage power stations, and established power plant planning models with different energy storage modes in different applications. These models are mostly based on evaluating economic benefits. In addition, the small world characteristics and scale-free characteristics of the power grid have also been studied in depth. Studies have shown that the increase of proportionality will gradually destroy the critical behavior of the system; the more frequent the occurrence of repeated crashes, the larger the scale of collapse.
Based on the above analysis, based on the research of the similarity of typical power grids, this paper conducts further research on the change of the proportional mixture after accessing the energy storage power station in the grid, aiming to find the internal mechanism that causes the difference of proportionality, in order to study the topology of the smart grid. The development of evolution and the critical behavior of the power system provide the basis.
(a) Grid topology
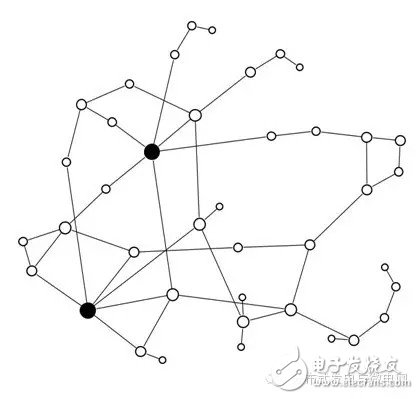
(b) Access to the topology of the energy storage power station

â— represents the hair node; â—‹ is the powered node
Figure 2 Grid topology of energy storage power station
in conclusion
Proportional hybridity is a special network topology feature, which is one of the important factors affecting the network's self-organized critical behavior. It is of great significance to study the structural vulnerability of power system, the inherent propagation mechanism of cascading failure and the corresponding dynamic behavior of power grid.
Through the analysis of the gl-mixing mode of different structural power grids, it is found that the difference between the topological structure and the functional positioning causes the difference in the non-proportional characteristics of the power grid. The power grid model based on NW small world network is designed. The distribution analysis of model proportional coefficient, feature path length and agglomeration coefficient shows that small world characteristics are the main factors causing some structural disproportionation.
In order to study the influence of different access modes of energy storage power stations on network topology, a storage model based on random and regular methods was designed. By analyzing the variation law of the proportional coefficient based on the actual network topology parameters, it is found that as the energy storage node is continuously connected to the network, the proportional coefficient is increasing, that is, the proportionality is enhanced. The increase in proportionality makes the distribution between different types of nodes in the network more “unevenâ€, which makes the grid's resistance to cascading failures decline.
Suizhou simi intelligent technology development co., LTD , https://www.msmvape.com