Three aspects of intelligent vehicle demand for ADAS
This article first talks about the demand of intelligent vehicles for ADAS, the special development environment of ADAS, and the development of ADAS control strategy, including vehicle modeling, ADAS system structure and parameters, and ADAS. Control algorithm development, ADAS HIL test system.
A smart vehicle is a comprehensive vehicle control system integrating environmental measurement and perception, vehicle positioning and attitude determination, local path and algorithm, networking and data interaction, planning decision-making and multi-level assisted driving. It integrates vehicle technology, Computers, modern sensing, information fusion, communications, artificial intelligence and automatic control technologies. Smart vehicles have become the focus of research in the field of vehicle engineering in the world and a new driving force for the growth of the automotive industry. The United States, Japan, and Europe have all incorporated them into their respective focused intelligent transportation systems.
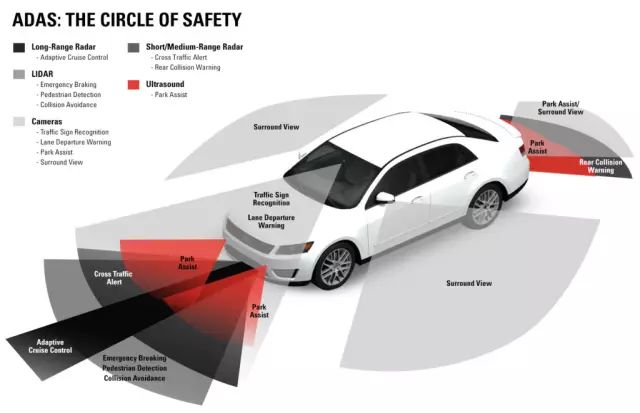
The first part influences the development of smart vehicles
ADAS
a) Competing demand of car companies: The functional features of the car, from the early electric windows to the latest ADAS system, the high-end features and functions of luxury cars have been applied to them over time. Mid-range and economy cars. Ford Focus cars in Europe now have features such as adaptive cruise control (ACC), automatic braking, and active lane keeping. Kia also has rear-view cameras.
b) The need for security policies: With the government's management needs for road safety, the government's road safety regulations and changes in the scoring system are also an important factor. The European automotive assessment agency "Euro NCAP" will begin to include pedestrian detection systems and brakes to reduce pedestrian injuries in 2016. A series of actions such as pedestrian detection and automatic braking will be tested. The U.S. National High Speed ​​Transport Security Administration is developing a policy of mandatory installation of rear view cameras and promotes the framework of car workshop communication.
c) Cost reductions and incentives: Discounts on insurance for vehicles with ADAS installed are another factor that drives the widespread use of ADAS. The decisive factor for the widespread use of ADAS in the automotive industry is the cost, the complexity of the technology, and the advancement of sensor and processor technology (in which few devices integrate multiple functions), so that today's economy cars can also withstand certain ADAS functions. Applications.
Smart car development environment
The development environment of the car mainly consists of a scene-based model and a control experiment for smart cars. The former mainly consists of the abstraction of various scenes to form a program environment; the latter mainly conducts experiments for research, calibration, and certification, including the experimental site. , laboratory equipment, speed environment and so on.
The function and application characteristics of the ADAS system are different from those of conventional automotive electronic control systems. The ADAS has its own characteristics:
1) The application scenario of ADAS is generally a closed loop system composed of people, vehicles, and roads. The three are indispensable.
2) ADAS is directly related to the performance of the vehicle, the characteristics of the road, and the safety behavior of the driver.
3) The ADAS system usually needs to cooperate with multiple on-board control systems and is a distributed control system.
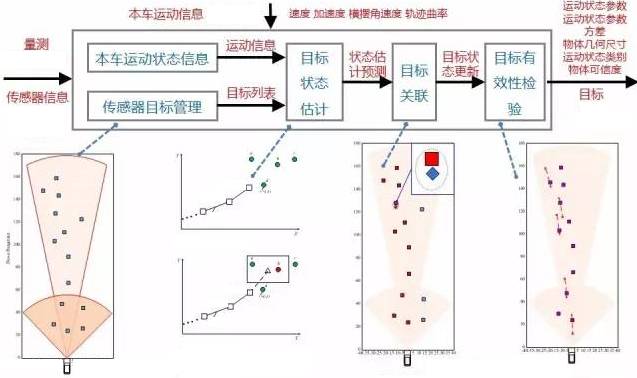
Longitudinal control requirements for vehicles
The development of the ADAS system is unique and follows the V-mode development process of the general ECU (tools and model-based design methods were first designed, simulated, and validated for the battery management control system and then the product code was generated for it) due to ADAS The real-time nature of the system is very important. It requires real-time data exchange with different types of sensors (such as cameras, lidar, radar, vehicle CAN bus, GPS, etc.), and it requires convenient integration of new functions and algorithms. The software development of ADAS system needs to solve many challenges, such as multi-thread programming, data sample time stamp and resynchronization, data delay measurement and estimation, system optimization and performance evaluation, code reuse and software application maintenance, etc. Consider a virtualized hardware-in-the-loop simulation test scheme.
ADAS is subdivided into different functions, but at present its test environment and solutions are used throughout the previous MBD modeling and algorithm development, until the release of ECU code, ECU prototypes are tested, connected to subsystems and sensors, and loaded onto prototypes. , As well as the formation of vehicles, sharing a test platform. From MIL, SIL to EIL, HIL, and VIL, a testing platform is used at all stages to reproduce the virtualized scene through software and test various functions of ADAS. Contains vehicle models, traffic environment models, driver models, sensor models, and environmental models. According to different test objects, different sensors are selected to obtain different information in the environment. The information obtained by the sensor is given to the algorithm or ECU, which in turn controls the entire vehicle in the environment to form a closed loop test environment. If you test early in the beginning of the algorithm, the test items will change as the development progresses later. If you use the test program from an early stage, the later stages will become more and more simple.
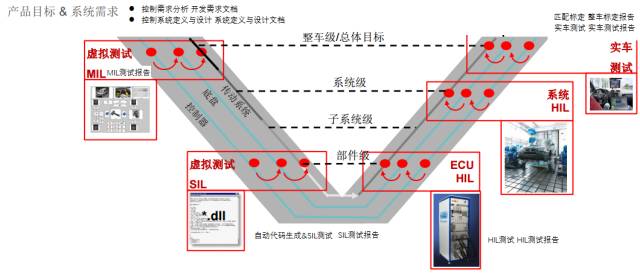
The development process of MBD (editors organize themselves)
Part II Control Strategy Development Process
ADAS Control Strategy Development
System-wide simulation modeling: Vehicle system dynamics focuses on the interaction of various forces that are encountered during vehicle travel, the resulting effects on vehicle movement, and the interaction between various systems within the vehicle.
Vehicle Modeling
Includes tire model and vehicle model. The former is a semi-empirical tire model based on experimental data. It has better fitting of the longitudinal force, lateral force and returning moment of the tire; the latter often needs to make some assumptions, such as the origin of the vehicle coordinate system coincides with the center of mass of the car; Only the longitudinal movement along the x-axis, the lateral movement along the y-axis, and the yaw movement about the z-axis; the mechanical properties of the tires are the same.
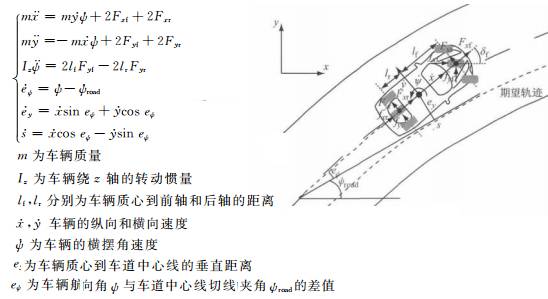
Traditional vehicle-based simplified model (editors organize themselves)
Now more and more began to build simulation models of the vehicle (Cruise simulation software, AMESim simulation software), including vehicle interior and exterior modeling, dynamic parameters and so on. AMESim can model and simulate the vehicle model with the traditional brake system, ABS and ESP system hydraulic and aerodynamic components and control schemes, and get more detailed results.
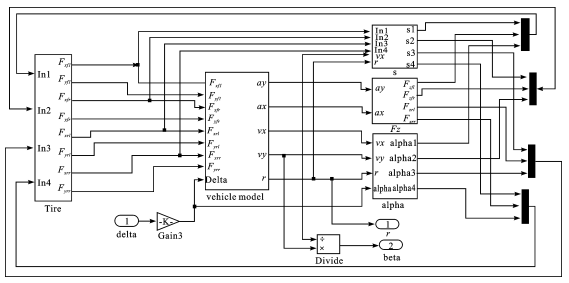
Vehicle model is further refined in software (AMESim modeling reference)
ADAS system structure and parameters: Using a sensor device, select a single camera and radar parameters selection. Based on these sensors, a multi-target tracking algorithm was developed to calculate effective distances, speeds, and angles of the target. It is necessary to further refine the parameters and variances of motion states, geometric dimensions, motion state categories, object feature category probabilities, etc., and also include sensors. Information and traffic environment information. Combine sensor measurement information, based on the motion information of the vehicle and the target management of the sensor, so as to estimate the state of the radar target, then correlate the data for each target, thereby correlating them into a valid object, and then the effectiveness of the object. The verification is performed to obtain the target motion state and motion state parameter deviation, geometry size, object reliability, and the like. Classify the movement of the object (the object is moving, stationary, start moving, and then start still).
Development of ADAS control algorithm: Take adaptive cruise as an example, including constant-speed battery life control, cornering cruise control, and follow-up control. The former control unit controls the vehicle to run at a constant speed in accordance with the cruising speed set by the driver; the latter maintains the relative speed of the host vehicle to follow the preceding target vehicle after the vehicle speed has dropped to the ideal target value. The three control systems are simultaneously calculated and then the ideal control output is selected based on the driving conditions of the vehicle. In practice, it is necessary to consider the dynamics and kinematics of the car itself, whether it is downhill or downhill, or the driving capability of different speed segments, etc., so as to limit the ideal control output.
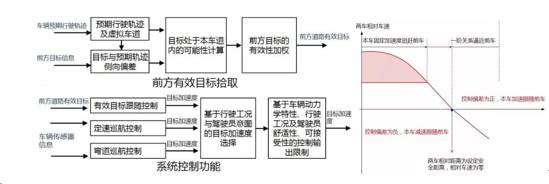
ACC front target and system function diagram (Source: Micro lecture "77GHZ millimeter wave big development difficulty")
The specific implementation is divided into Simulink after sub-module implementation, and PID control strategy is implemented within the constant-speed module.
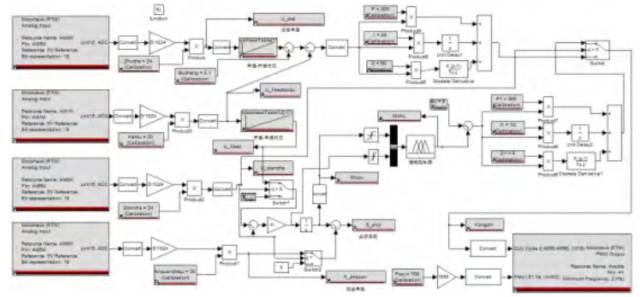
ACC algorithm Simulink implementation (end editors organize themselves)
ADAS HIL Test System: Many automotive OEM companies have adopted a complete "virtual vehicle" testing platform and completed the ADAS simulation test. Through the real-time operation of the simulation model of the vehicle to be tested, the vehicle can be simulated in various operating states and various complex operating conditions, and the manual and automated testing of the vehicle's electronic and electrical system can be completed.
Shenzhen Hongyian Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.hongyiancon.com