The working principle of the relay and the analysis of the drive circuit - the circuit diagram is read every day (245)
A relay is an electronic control device that has a control system (also called an input loop) and a controlled system (also called an output loop). It is usually used in an automatic control circuit. It actually uses a small current to control the larger. An "automatic switch" of current. Therefore, it plays the role of automatic adjustment, safety protection and conversion circuit in the circuit.
Relay characteristics of relays
The input signal x of the relay is continuously increased from zero to the action value xx when the armature starts to pick up. The output signal of the relay immediately jumps from y=0 to y=ym, that is, the normally open contact is disconnected to open. Once the contact is closed, the input x continues to increase and the output signal y will no longer change. When the input quantity x drops from a value greater than xx to xf, the relay begins to release and the normally open contact opens. We call this characteristic of the relay a relay characteristic, also called the input-output characteristic of the relay.
First, the working principle and characteristics of the relay
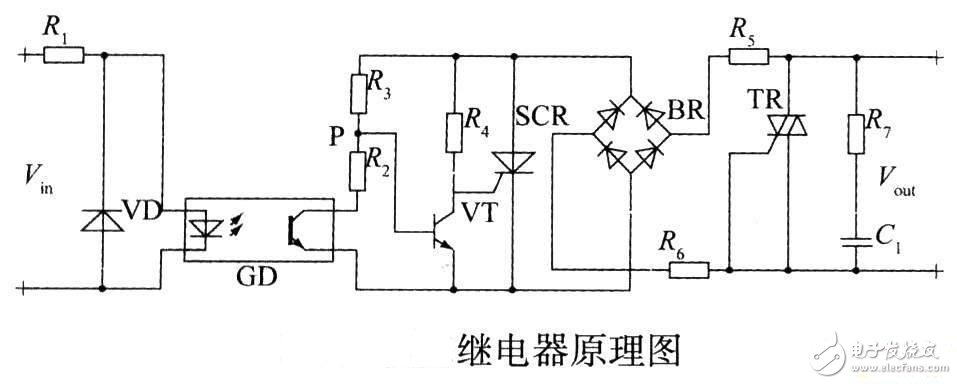
1. Working principle and characteristics of electromagnetic relay
Electromagnetic relays are generally composed of a core, a coil, an armature, a contact spring, and the like. As long as a certain voltage is applied to both ends of the coil, a certain current flows in the coil, thereby generating an electromagnetic effect, and the armature will absorb the pulling force of the return spring against the iron core under the action of the electromagnetic force attraction, thereby driving the armature. The moving contact is in contact with the stationary contact (normally open contact). When the coil is de-energized, the electromagnetic suction also disappears, and the armature will return to the reaction force of the spring.
Return to the original position and release the moving contact with the original static contact (normally closed contact). In this way, the suction and release are achieved, thereby achieving the purpose of turning on and off in the circuit. For the "normally open, normally closed" contacts of the relay, it can be distinguished as follows: a static contact that is in an open state when the relay coil is not energized, called a "normally open contact"; a static contact that is in an on state It is a "normally closed contact".
2, the circuit principle
2.1 Brief introduction of relay
basic concept
The relay is a kind of contact current (or circuit) that turns on or off the AC and DC small capacity control loop when the input quantity changes to a certain value.
2.2 Working principle
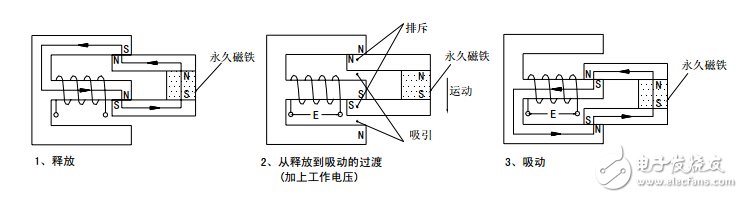
The permanent magnet keeps the release state, and after the working voltage is applied, the electromagnetic induction causes the armature and the permanent magnet to generate suction and repulsive moments, generates downward movement, and finally reaches the suction state.
3, transistor drive circuit
3.1 Circuit Schematic
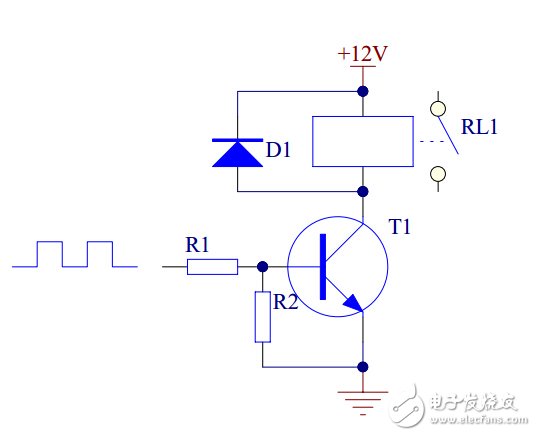
When a transistor is used to drive a relay, an NPN transistor is recommended. The specific circuit is as follows:
Introduction to working principle
When the input level is high, the transistor T1 is saturated and the relay coil is energized, and the contacts are attracted.
When the input is low, the transistor T1 is turned off, the relay coil is turned off, and the contact is turned off.
3.2 The role of each component in the circuit
Transistor T1 is a control switch.
The resistor R1 mainly acts as a current limiting device to reduce the power consumption of the transistor T1.
Resistor R2 reliably turns off transistor T1.
Diode D1 reverses the freewheeling flow, providing a bleed path for the triode to turn off the relay coil and turn its voltage across +12V.
4, integrated circuit drive circuit
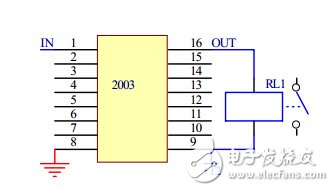
Integrated circuits integrated with multiple drive transistors have been used, and the use of such integrated circuits simplifies the design process of printed boards that drive multiple relays. At present, the integrated circuits for driving relays used by our company mainly include TD62003AP.
When the input end of 2003 is high level, the corresponding output port outputs a low level, the relay coil is energized at both ends, and the relay contacts are attracted;
When the input of the 2003 is low, the corresponding output port is in a high impedance state, the relay coil is powered off at both ends, and the relay contact is disconnected.
24V relay drive circuit
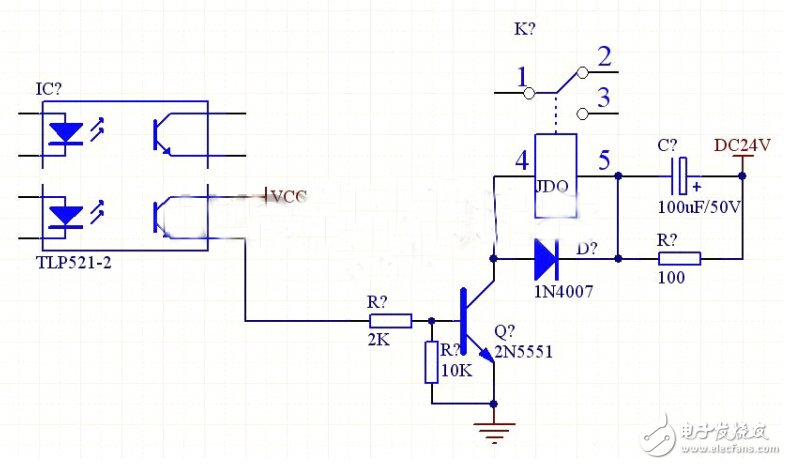
Relay series RC circuit: This form is mainly used in circuits where the rated operating voltage of the relay is lower than the supply voltage. When the circuit is closed, the self-inductance of the relay coil will cause the electromotive force to hinder the increase of the current in the coil, thereby prolonging the pull-in time. After the RC circuit is connected in series, the pull-in time can be shortened. The principle is that at the moment when the circuit is closed, the voltage at the voltage across the capacitor C cannot be abruptly changed as a short circuit, so that a power supply voltage higher than the rated working voltage of the relay coil is applied to the coil, thereby accelerating the speed of the current increase in the coil, so that the relay Quickly pull in. Capacitor C does not work after the power supply is stable, and resistor R acts as a current limiter.
Second, the selection of the rated working voltage of the relay
The rated operating voltage of the relay is one of the most important technical parameters of the relay. When using a relay, you should first consider the operating voltage of the circuit in which it is located (ie, the circuit in which the relay coil is located). The rated operating voltage of the relay should be equal to the operating voltage of the circuit in which it is located. The operating voltage of the circuit is generally 0.86 of the rated operating voltage of the relay. Note that the workpiece voltage of the circuit should not exceed the rated working voltage of the relay, otherwise the relay coil is easy to burn. In addition, some integrated circuits, such as the NE555 circuit, can directly drive the relays. Some integrated circuits, such as COMS circuits, have a small output current. A transistor amplifier circuit is required to drive the relay. This should consider that the transistor output current should be greater than The rated operating current of the relay.
1, transistor drive circuit
When a transistor is used to drive a relay, the emitter of the transistor must be grounded. The specific circuit is as follows:
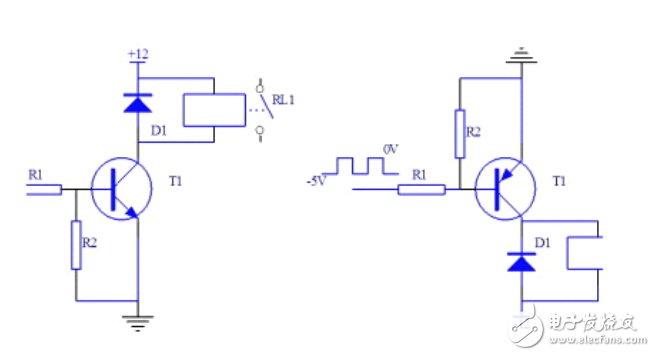
2, principle introduction
When the NPN transistor is driven: When the base of the transistor T1 is input to a high level, the transistor is saturated and the collector becomes low, so the relay coil is energized and the contact RL1 is pulled. When the base of the transistor T1 is input to a low level, the transistor is turned off, the relay coil is turned off, and the contact RL1 is turned off.
Edit Comment : This paper introduces the working principle of the relay and the drive circuit of the relay. The design of the drive circuit should be based on the pull-in voltage and current of the relay coil used. It must be greater than the pull-in current of the relay to make the relay work reliably.
Electronic enthusiasts "Automotive Electronics Special", more quality content, download now 
General Purpose Steel Wire Rope
Aircraft Cable And GP Steel Wire Rope
Widely used in the industry of Port Machinery, Vessels, Elevators, Engineering Machinery, Mining, Petroleum, etc
GAC: 7x7 7x19
GP steel wire rope: 1x7 1x19 6x7 7x7 6x19 7x19 6x12 6x24 6x37
Surface: (1) hot-dip galvanized; (2) electric galvanized; (3) black; (4) PVC coating; (5) stainless steel; (6) zinc + aluminum, etc.
Steel Wire Rope,Galvanized Wire Rope,Galvanized Steel Wire Rope,Galvanized Aircraft Cable
ROYAL RANGE INTERNATIONAL TRADING CO., LTD , https://www.royalrangelgs.com