Talk about battery management system
Under the background of the government's mandatory parallel management of fuel consumption and new energy vehicle points, a large number of car companies have launched new energy vehicle development and listing plans, and will continue to increase. In order to meet this series of plans, in the PHEV (including EREV), EV areas, automotive companies need to use different combinations of new energy vehicles to meet policy norms, meet market demand and cater to consumers, which requires models The core indicators (shipping mileage, 100km acceleration and charging speed) are dynamically configured and managed and can handle future battery supplier conversions. In this process, we carefully talk about the value of the battery management system, and how to do the battery management system.
This article refers to the address: http://
The first part of the modular supply
In short, with the development of the electric vehicle industry, China may also introduce the lithium battery standard for automobiles like the German VDA. The standardization of battery cells and modules is imperative. Through the series, parallel or series-parallel mixing of the battery cells, the uniform size of the battery module is ensured, and the mechanical characteristics, thermal characteristics and safety characteristics of the battery body are comprehensively considered. Different battery capacities are available to meet different needs according to different cruising range and power requirements with the same installation design. This modular application enables large-scale automated production on both the single and module sides, significantly reducing production costs, which makes the entire battery company supply the smallest module.
Modular supply has changed the way the original battery companies were built. Originally, the battery cells were supplied, and the car companies needed to build from the single unit. The topology of the entire BMS should be balanced according to the battery size, and under the supply module conditions. The basic unit becomes a small module assembly.
In this process, the next integrated battery module accommodates a larger capacity battery pack than a conventional electric vehicle module. In the past, battery modules generally consisted of 12 battery packs with a capacity of 2-3 kWh, and now they are turning to a 6-8 kWh battery pack that can hold 24 units. This will increase the battery capacity in the same battery space and effectively increase the battery life.
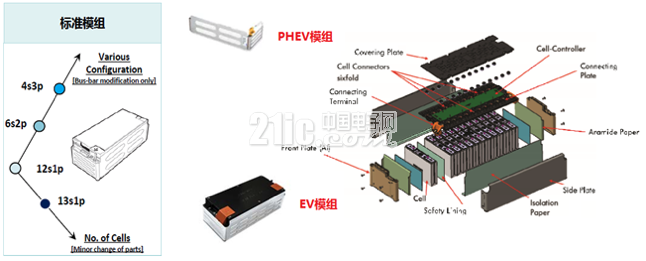
Figure 1 PHEV and EV modules
The basic situation of the soft pack is similar, and it has begun to develop in this direction.
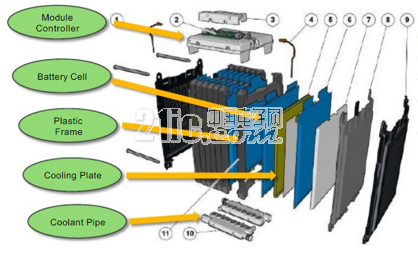
Figure 2 Soft package module
As shown in Figure 3, the module has built-in LECU function, which basically eliminates module temperature acquisition and single voltage acquisition and voltage protection.
· Single cell voltage measurement and voltage monitoring: the collection and protection of the voltage of the cell, this function is down to the bottom. Here is divided into:
Collecting cell voltage: Accuracy affects the comparison of monomer differences
Discrimination of overvoltage and undervoltage: here is also the logic function that can be done underneath
Verification: Diagnose processing of the entire function by means of monomer accumulation and module voltage discrimination
·Battery temperature: Now usually 2-4 temperature points are placed in one module to collect busbar soldering temperature and battery temperature difference in the module.
Communication and signal: send temperature and voltage information, and send basic single-voltage overvoltage and undervoltage
· Balanced actual control: mainly contains the actual circuit

Figure 3 LECU and its basic functions
The second part of the battery management function
As mentioned earlier, due to changes in the supply model, the battery management function needs to match the entire battery system, and the underlying basic components become modules. The issues facing automotive companies here are:
·The difference in demand of the whole vehicle power system: according to the actual configuration of different vehicles, there are different requirements for the discharge capacity and power characteristics of the battery.
·Charging characteristics: According to the actual situation of use, you can customize the special needs of charging
·Regional use characteristics: It is even necessary to configure different thermal management characteristics depending on the environment in which the vehicle is used.
·The difference in modules may vary depending on the needs of the vehicle. It is necessary to switch the chemical system of the monomer.
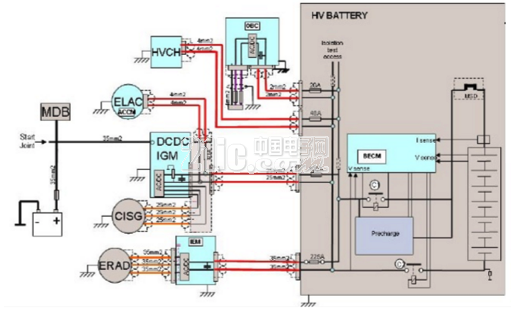
Figure 4 High-voltage system architecture
As a result, the demand for control of BMS by vehicle manufacturers is obvious:
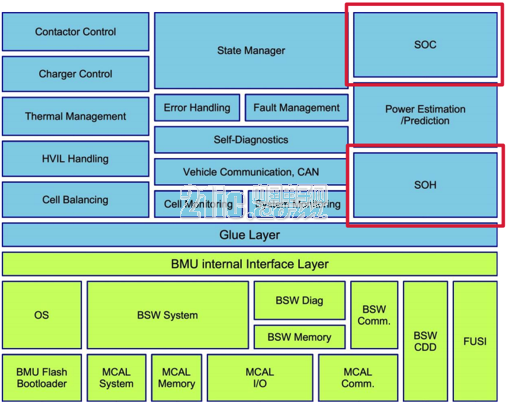
Figure 5 battery management system kernel
Here, it is divided into "variable parts" and "immutable parts", among which the common parts are:
1) Battery parameter detection:
Including total voltage, total current, insulation detection (monitoring leakage), collision detection, etc.
· Total voltage measurement: When calculating the SOC later, it is often calculated by using the total voltage of the battery pack. This is one of the important parameters for calculating the battery pack parameters. If the single voltage is accumulated, the battery voltage sampling is There is a certain time difference, and there is no way to accurately align with the data of the battery sensor. Therefore, the battery pack voltage is often collected as a main parameter for calculation. When diagnosing the relay, it is necessary to compare the voltage inside and outside the battery pack.
· Total current measurement: The current measurement method is mainly divided into two kinds of intelligent shunt or Hall current sensor. Since the current value that the battery system needs to process is often very large, such as the discharge current required for vehicle acceleration and the charging current when energy is recovered, it is necessary to evaluate the output current (discharge) and input current (charge) of the battery pack. Range and accuracy.
Insulation resistance detection: It is necessary to conduct insulation test on the whole battery system and high voltage system. It is relatively simple to rely on the bridge to measure the insulation resistance of the bus positive and negative ground to ground. Active signal injection can also be used, mainly to detect the insulation resistance of the battery cell to the system.
High-voltage interlock detection (HVIL): used to confirm the integrity of the entire high-voltage system (which can be divided into two parts, the discharge circuit and the charging circuit). When the high-voltage system circuit is broken or the integrity is damaged, it is necessary to start safety. The measure is gone.
SOC and SOH estimation: including state of charge (SOC) or depth of discharge (DOD), state of health (SOH), functional state (SOF), energy state (SOE), fault and safety state (SOS), etc.
2) Fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant operation
· Fault detection refers to the analysis of the collected sensor signals, the use of diagnostic algorithms to diagnose fault types, and early warning. Battery failure refers to sensor failures of various subsystems such as battery packs, high-voltage electrical circuits, and thermal management, actuator failures (such as contactors, fans, pumps, heaters, etc.), as well as network failures, various controller hardware and software failures. Wait. The fault of the battery pack itself refers to overvoltage (overcharge), undervoltage (overdischarge), overcurrent, ultrahigh temperature, internal short circuit fault, loose joint, electrolyte leakage, and insulation reduction.
· The fault of the battery management unit also needs to be alarmed by the DTC. The DTC triggers the indicator light in the instrument panel. In the new energy vehicle, the battery fault also has corresponding indicator light to remind the driver. Due to the danger of the battery, it is often necessary to directly transmit information to the car system to cope with sudden accidents. For example, when an accident occurs, when the airbag is ejected and the relay is directly cut off by the vehicle controller, the car system is handled by positioning and early warning, especially the battery is discharged. Fault diagnosis includes diagnosis of battery cell voltage, battery pack voltage, current, battery pack temperature measurement circuit faults, determination of fault location and fault level, and corresponding fault tolerance control.
· Fail-Safe's fault-tolerant operation mechanism refers to the degraded operation of the vehicle after the vehicle encounters an error during operation. In fact, this feature is more like degrading and backing up all of the above features. This mechanism includes fault detection, fault type judgment, fault location, and fault information output.
3) Relay control
· Control the battery pack generally has multiple relay systems to complete the drive supply and status detection of the relay. The relay control is often coordinated with the vehicle controller to confirm the controller, and the collision signal output by the airbag controller is generally combined with the relay controller. Disconnect the direct hook. The relays in the battery pack generally have main positive, main negative, pre-charge relays and charging relays. There is also a separate power distribution box outside the battery pack to provide a more detailed protection for the entire current distribution. The relay control of the battery pack, the state of closing, opening, and the order of the switches are all important.
Variable part:
1) Thermal management:
• It is necessary to detect the temperature parameters of the battery pack thermal management system (temperature of the fluid inlet and outlet), and the detection circuit is similar to the monomer detection. According to the temperature distribution information and charge and discharge requirements in the battery pack, the intensity of active heating/heat dissipation is determined, so that the battery works as much as possible at the most suitable temperature, and the performance of the battery is fully exerted.
· Thermal control: The chemical performance of the battery is greatly affected by the temperature of the environment. In order to ensure the service life of the battery, the battery must be operated within a reasonable temperature range, and the vehicle controller can output its output according to different temperatures. And the maximum power input. For the temperature control of the battery system, CFD simulation analysis is mainly used. The core here is to select different external methods of thermal management, and then the internal temperature management threshold is used to ensure that the temperature threshold is available.
Figure 6 Liquid and air cooling share a basic BMU system
2) Charge control
One of the main modes of the original battery management system is to monitor the battery system's demand during the charging process, and to be responsible for the current input of the entire battery system, including the control of conventional charging and energy recovery. Now the variable part is designed for fast charging. Due to the needs of consumers and the actual situation, this place is also in a very high change area.
3) Balance management:
In the actual use of the battery packs connected in series, the output capacity of each series is different. The battery has not only the limitations of overdischarge and overcharge, but also the input and output power at different temperatures and different SOCs. That is to say, the limitation of a single battery will affect the entire battery.
· Individual differences between individual cells in the battery pack: difference in monomer capacity, difference in monomer internal resistance, difference in self-discharge of the monomer, current difference during operation, and current difference during sleep
·The battery pack's monomer capacity, monomer internal resistance, and monomer self-discharge will change with time.
·Customer use: charging time, discharge time
· External environment: self-discharge at the same temperature, self-discharge under different SOC
· System interaction: The working condition of the BMS, this factor is related to the working status of the BMS.
When the actual battery capacity changes greatly, the upper end of the BMU needs to give different strategies when the equalization capability is determined to be dead.
Therefore, the possible change in the future is that the battery management system forms a separation between the lower end and the upper end. For a large number of projects, saving management and change management, the automobile factory needs to form Party B in Party A, and the part that specializes in system software is responsible for The core algorithm and configuration process for the entire battery system management, they are responsible for setting the battery protection and usage thresholds, responsible for the availability and after-sales of the entire vehicle. The hardware management of the entire BMS, but it has nothing to do with the car companies, here need very good hardware and software interface files, otherwise it is extremely error-prone. The things we control in the future are quite limited.
The production process of a machine is the whole process of making a product from a raw material (or semi-finished product). For machine production, it includes the transportation and preservation of raw materials, preparation for production, the manufacture of blank, the processing and heat treatment of parts, the assembly and debugging of products, paint and packaging. The content of production process is very extensive. Modern enterprises use the principles and methods of systems engineering to organize production and guide production, and regard the production process as a production system with input and output.
The technological process
The technological process
In the production process, the process of changing the shape, size, position and nature of the production object, so that it becomes a finished product or semi-finished product is called the technological process. It is an essential part of the production process. Process: casting, forging, stamping, welding, machining, assembly processes, such as machinery manufacturing process generally refers to the part machining process and machine of the sum of the assembly process, other process is known as the auxiliary process, such as transportation, storage, power supply, equipment maintenance, etc. The technological process is composed of one or several sequential processes, and a process is composed of several working steps.
Working procedure is the basic unit of mechanical processing process. The so-called process refers to a (or a group of) workers, in a machine tool (or a working place), on the same workpiece (or at the same time to several workpiece) of the continuous completion of that part of the process. The main characteristic of a process is that it does not change the processing object, equipment and operator, and the content of the process is continuously completed.
Precision Cnc Machining,Cnc Machining Parts,Custom Cnc Machining,Precision Cnc Turning Parts
Tianhui Machine Co.,Ltd , https://www.thcastings.com